Art Pottery: A History of the Field and a Look at Celebrated American Artists
Summary
Reflection Questions
Journal Prompt
Historically rooted in the production of utilitarian objects, art pottery has evolved over centuries into a decorative and artistic medium, reflecting a fusion of form, function, and beauty. This evolution chronicles a journey from everyday household items to sophisticated works of art, embodying cultural, artistic, and technical advancements. Art pottery, in its diverse manifestations, now stands as a testament to the creative spirit, showcasing the intricate interplay between artist, material, and technique. In this article, we examine the rich history and celebrated artists of American art pottery, tracing its transformation and enduring significance.
The Origins and Evolution of Art Pottery


The origins of pottery date back to ancient civilizations, where it primarily served functional purposes. Early pottery, found in archaeological sites worldwide, was used for storing food, carrying water, and cooking. These utilitarian objects were often simply adorned but gradually exhibited signs of artistic consideration.
The earliest forms, made by hand and later on the wheel, displayed basic forms of decoration like incising and pinching, indicating the beginning of pottery’s journey towards an art form. The aesthetic elements in these early clay body pieces, though secondary to function, laid the groundwork for the evolution of pottery into a more expressive medium.
Fuel your creative fire & be a part of a supportive community that values how you love to live.
subscribe to our newsletter
*please check your Spam folder for the latest DesignDash Magazine issue immediately after subscription


Transition from Utilitarian to Decorative and Expressive Art in Various Cultures
Over time, different cultures began to place greater emphasis on the decorative aspects of pottery. In ancient Greece, for instance, pottery became a canvas for intricate narrative scenes and geometric designs, exemplifying its shift towards an art form.
In Asian cultures, particularly China and Japan, the development of sophisticated glazing techniques and the rise of tea ceremony culture led to pottery that was both functional and highly artistic. This transition was marked by a growing appreciation for the aesthetic qualities of pottery, with its form, color, and texture gaining importance equal to its function.
Influence of Historical Events and Cultural Movements on the Development of Art Pottery
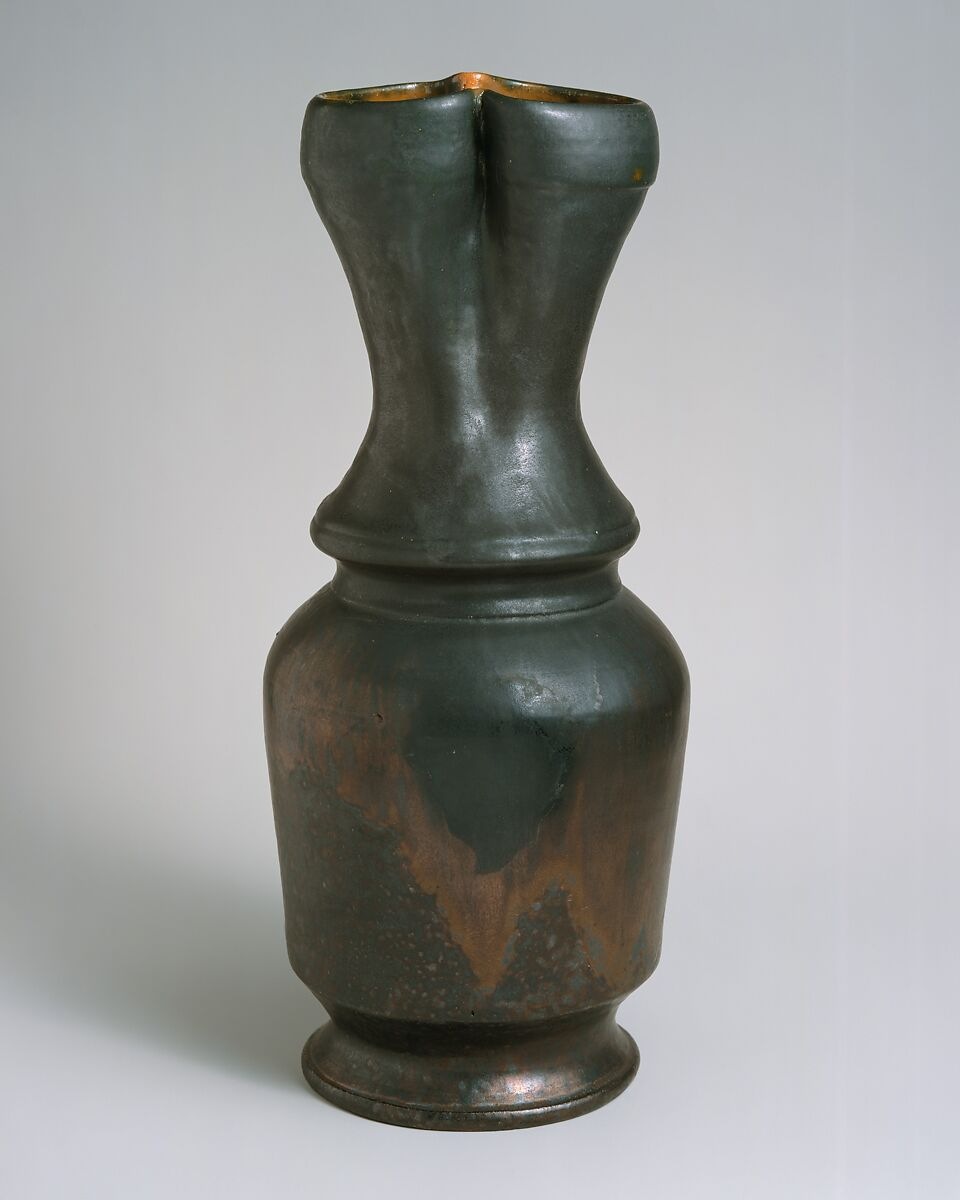


The development of art pottery was significantly influenced by various historical events and cultural movements. The Industrial Revolution, for example, introduced mass production of ceramic ware, leading artists to react against the loss of individual craftsmanship. This reaction gave birth to movements like the Arts and Crafts movement in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, emphasizing handcrafted pottery with artistic integrity.
Similarly, cultural exchanges between the East and West introduced new styles and techniques, fostering innovation in pottery design. The 20th century saw the emergence of studio pottery, where individual artists experimented with form and glazing techniques, pushing pottery firmly into the sphere of fine art. These historical and cultural shifts played a pivotal role in shaping art pottery into the diverse and expressive medium it is today.
Major Movements and Styles in Art Pottery
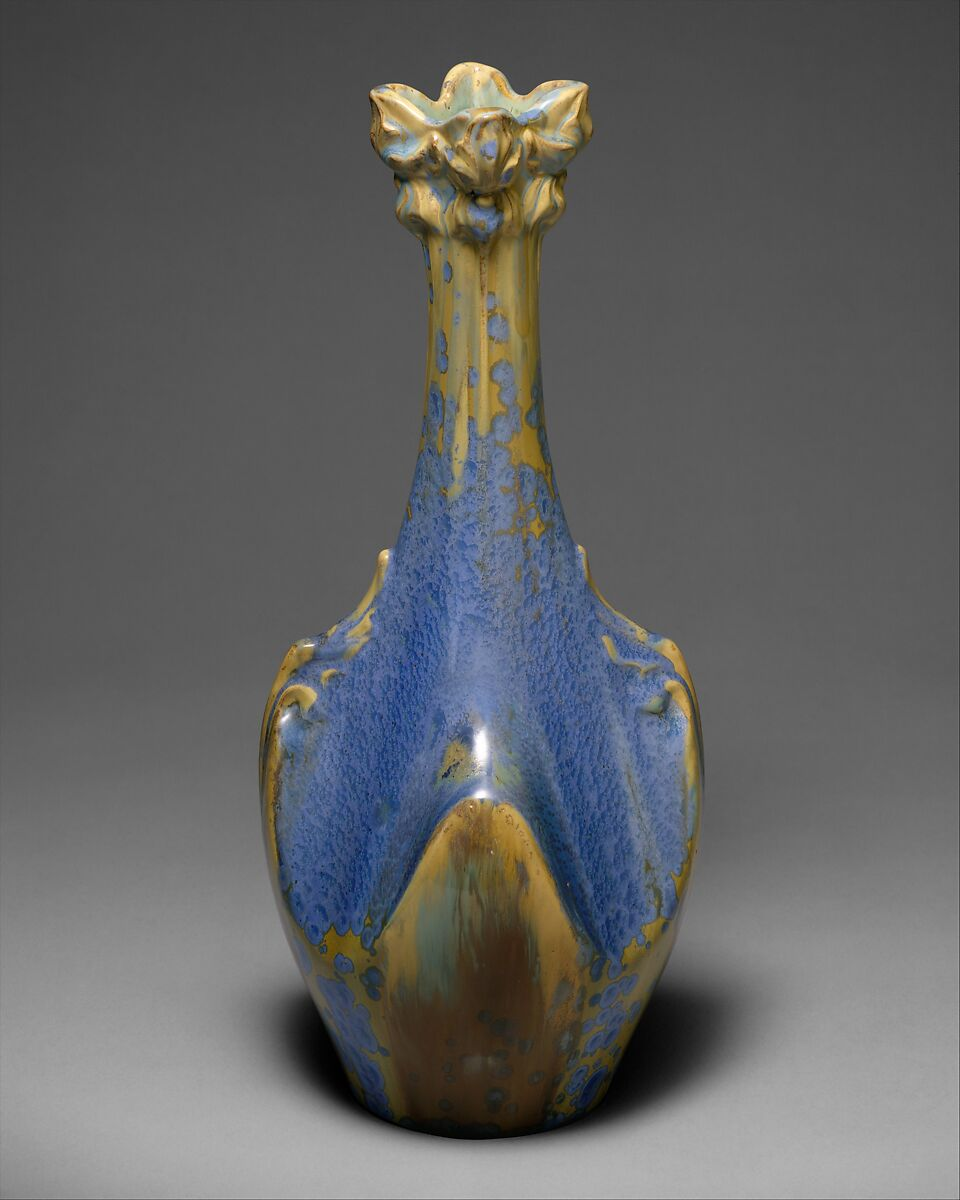


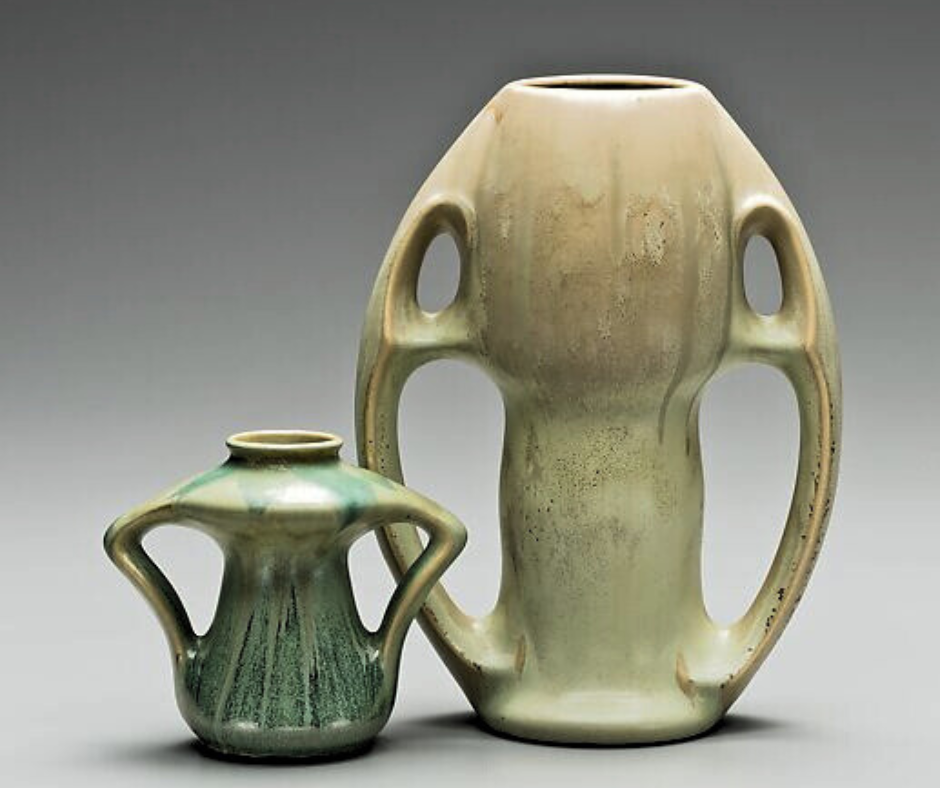
Arts and Crafts Movement: Originating in the late 19th century, this movement was a reaction against the industrial mass production of goods. It emphasized handcrafted artistry and natural materials, leading to pottery that showcased simplicity and functional beauty. This style is known for its simplicity, sturdy forms, and matte glazes. Arts and Crafts pottery often features earthy colors and emphasizes the beauty of the material and craftsmanship.
Art Nouveau: Flourishing between 1890 and 1910, Art Nouveau pottery was characterized by organic, flowing lines and often included natural motifs like plants and flowers. This style of decorative pottery was a departure from historical and classical motifs, focusing on free-form and natural designs. It is distinguished by its ornate, curvilinear designs and use of bold, often iridescent, colors. Pottery in this style frequently includes intricate, flowing designs inspired by the natural world.
Studio Pottery Movement: Gaining momentum in the 20th century, the Studio Pottery Movement was marked by individual potters and artists who focused on unique, handcrafted pieces. This movement celebrated the artist as an individual craftsman, giving rise to one-of-a-kind art potteries that were as much art as they were functional items. Studio pottery is diverse, reflecting each artist’s personal style. Common characteristics include a focus on organic forms, experimental glazes, and techniques that highlight the hand of the artist, such as visible brush strokes or the marks of the potter’s wheel.
Impact of These Movements and Styles on the Evolution of Art Pottery
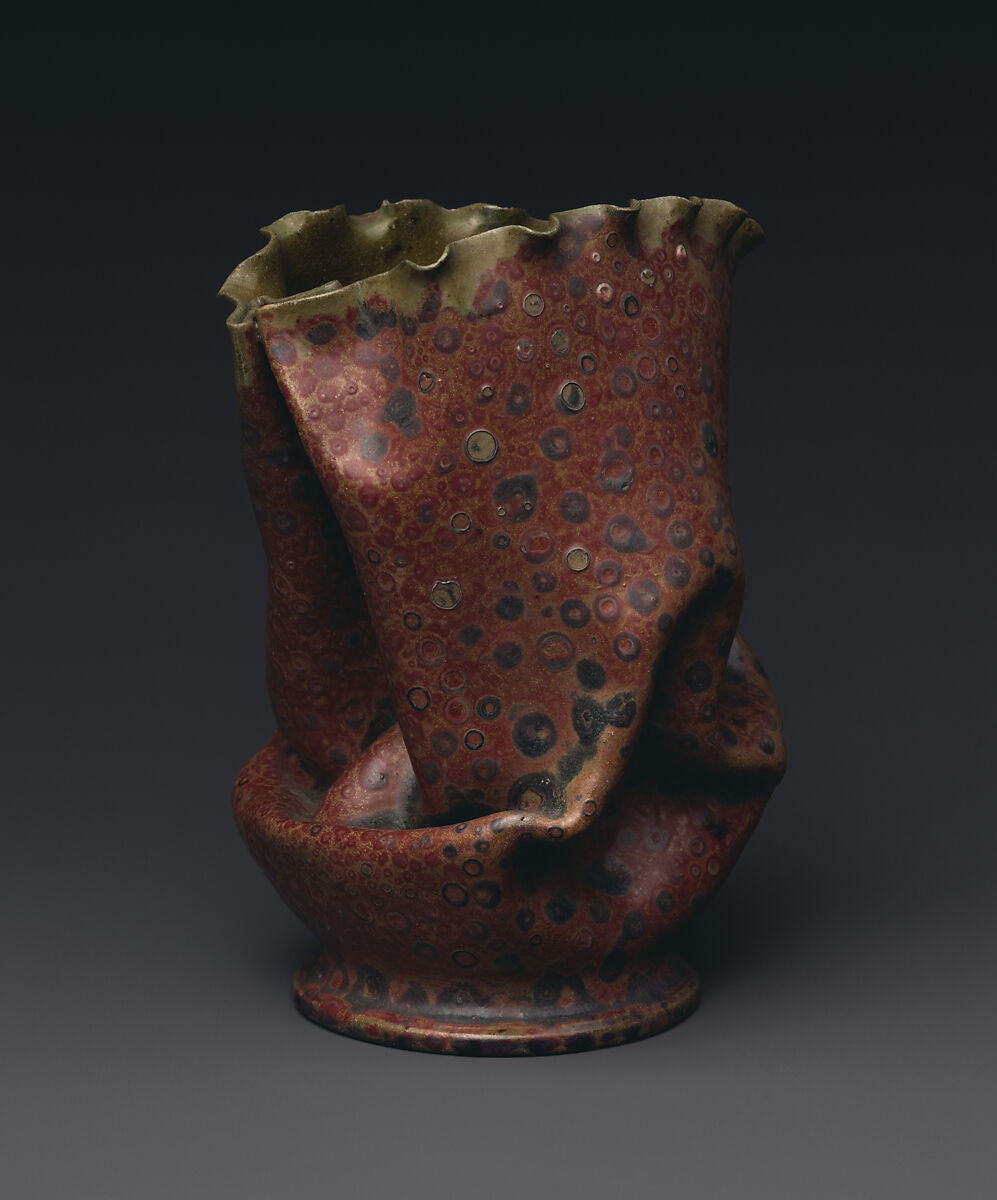


The Arts and Crafts Movement brought the focus back to individual craftsmanship and the inherent beauty of handcrafted pottery, influencing a return to traditional techniques and fostering a new appreciation for artisanal pottery. The Art Nouveau Movement revolutionized pottery aesthetics, encouraging creativity and the exploration of new forms and designs. It paved the way for more artistic freedom in pottery and influenced later styles that valued artistic expression.
The Studio Pottery Movement had a significant impact on how pottery was perceived in the art world. It elevated pottery to the status of fine art and encouraged potters to explore their medium as a form of personal artistic expression. These movements and styles played crucial roles in transforming pottery from functional craft to an art form, expanding the boundaries of what pottery could be and influencing generations of potters and ceramic artists.
Techniques and Innovations in Art Pottery
Exploring the realm of art pottery reveals a rich tapestry of techniques and innovations that have evolved and diversified over time, significantly influencing the medium’s artistic expression. Below are a few techniques still used in modern ceramics.
Throwing: One of the most traditional techniques, throwing involves shaping clay on a potter’s wheel. This method allows for the creation of symmetrical and rounded forms and requires significant skill to master the balance and movement of the clay.
Hand-Building: This includes techniques like coiling, pinching, and slab building. Hand-building offers more freedom in terms of shape and size, allowing artists to create more abstract and asymmetrical pieces.
Glazing: The application of glazes (liquid glass) adds color, texture, and functionality to pottery. The choice of glazes and application techniques can drastically change the appearance of a piece, with options ranging from matte to glossy finishes and from monochrome to intricate multicolored patterns.
Firing: The process of firing earthenware in a kiln hardens the clay and sets the glaze. Firing techniques and temperatures vary widely, with different methods such as raku, pit firing, or high-temperature stoneware firing producing distinct results.
Innovations in Materials and Methods Over Time
Over the centuries, there have been significant innovations in both materials and methods in pottery. The development of new clay bodies, such as porcelain, expanded the possibilities in terms of texture and durability. The evolution of glazing techniques and the creation of new glaze formulas have allowed for a wider range of finishes and effects, from subtle earth tones to bright, intricate designs. Advances in kiln technology have also had a major impact, with modern kilns allowing for more precise temperature control, leading to more consistent and diverse firing results.
How Technological Advancements Have Influenced Art Pottery
Technological advancements have greatly expanded the potential of art pottery. Digital tools, such as 3D printing and computer-aided design, have opened up new possibilities for form and complexity, allowing artists to create designs that would be impossible to achieve by hand.
Modern materials science has also contributed to the development of new clays and glazes, offering a broader palette for artistic expression. Furthermore, the internet and social media have had a profound impact on the field of art pottery, providing a platform for artists to share their work, gain inspiration, and connect with audiences and markets worldwide.
The field of art pottery is characterized by a rich blend of traditional techniques and contemporary innovations. This dynamic interplay between the old and the new continues to push the boundaries of what can be achieved in this timeless art form.
Art Pottery in Different Cultures
Art pottery, with its rich and diverse expressions, reflects the cultural heritage and artistic philosophies of different regions around the world. Each tradition offers unique insights into the materials, techniques, and aesthetics valued by various cultures.
Japanese Raku
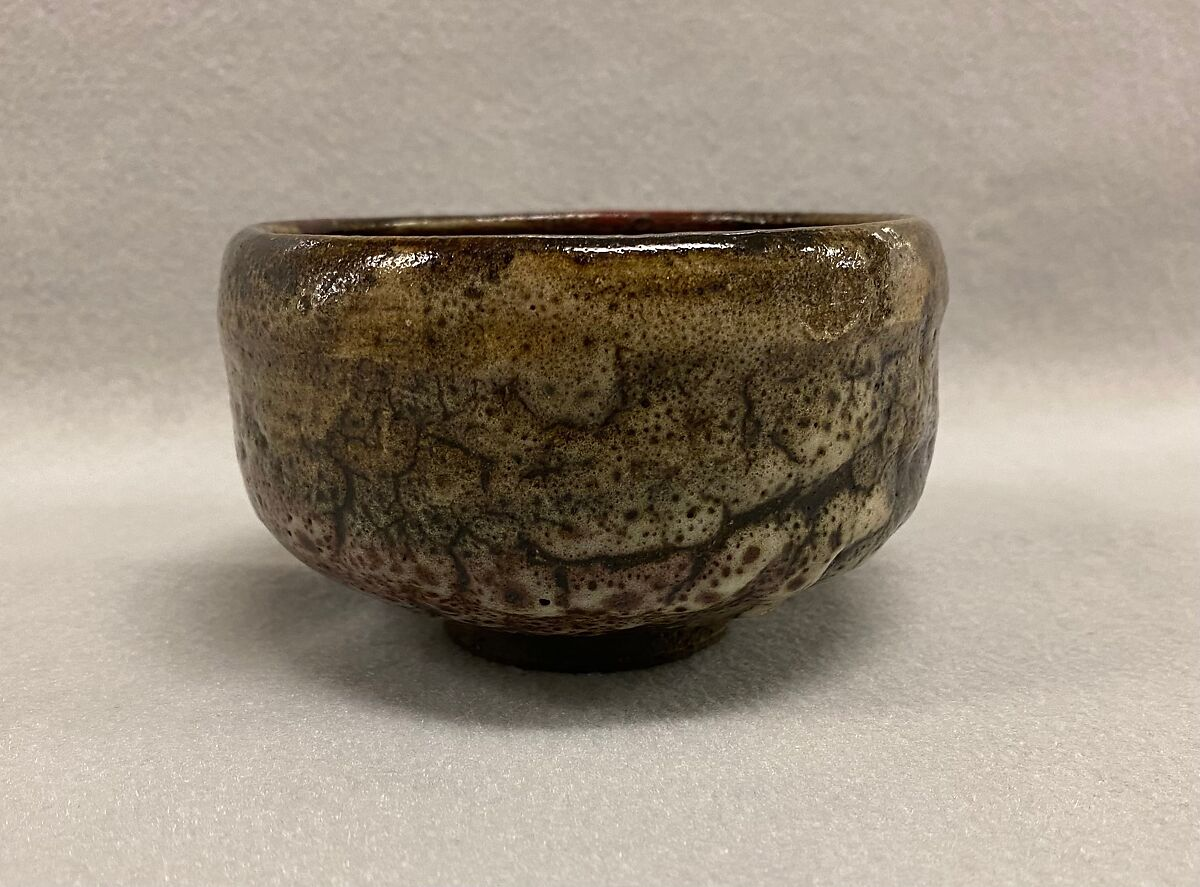


Beyond the Western world, we have the Japanese art of Raku pottery. Raku pottery, originating in 16th-century Japan, is known for its intimate hand-building process and low-temperature firing. These pieces are typically made in very small quantities. This technique was closely associated with the Japanese tea ceremony and emphasized simplicity and naturalness.
Whether bowls or other vessels, Raku wares are characterized by their rustic appearance, with glazes that range from earthy to vibrant. The unpredictable nature of raku firing, where pieces are removed from the kiln while hot and subjected to post-firing reduction, results in unique, often surprising textures and colors. The philosophy behind raku resonates with the Japanese aesthetic of wabi-sabi, embracing the beauty in imperfection and transience.
Chinese Porcelain
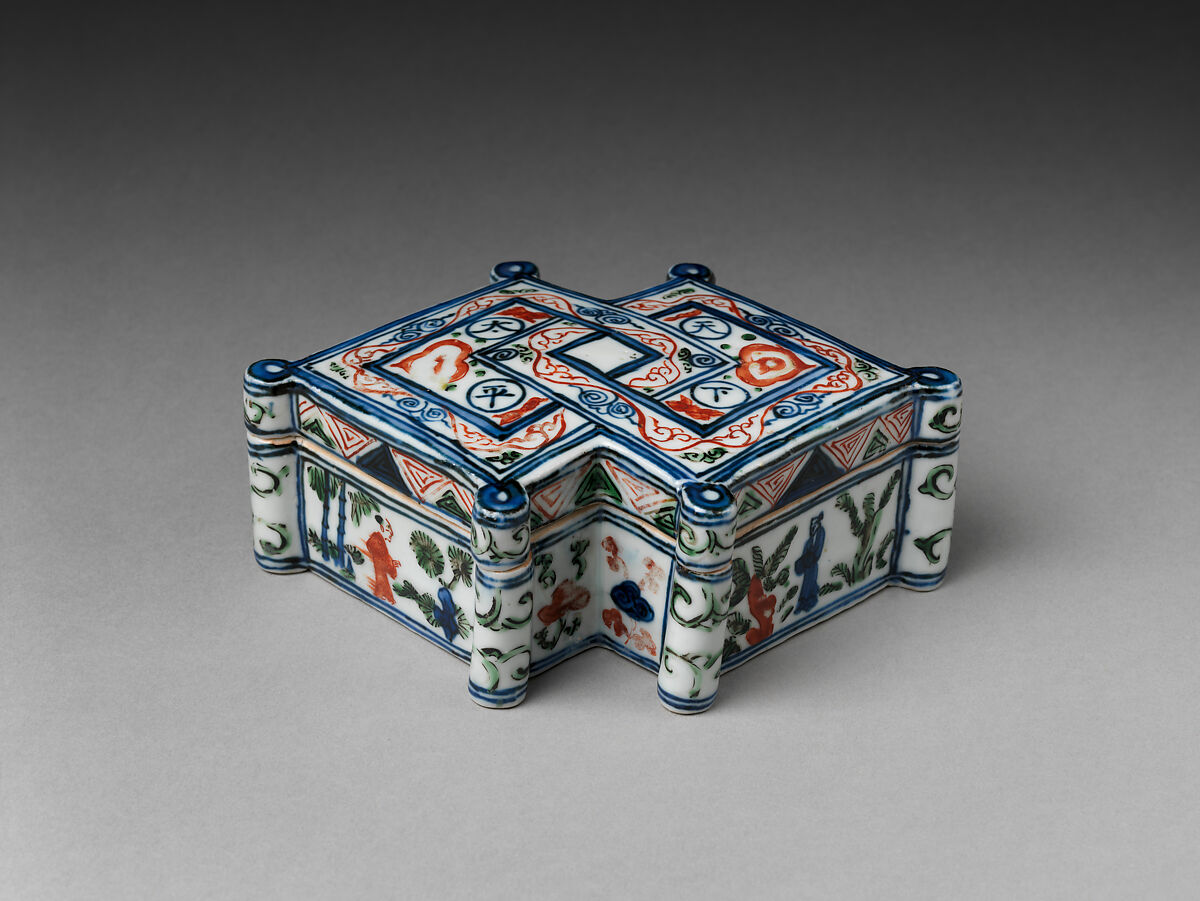


Chinese porcelain, developed during the Tang dynasty and perfected in the Ming and Qing dynasties, is famed worldwide for its sophistication and quality. It represented a significant technological advancement in pottery, with its high firing temperatures and refined clay.
Known for its white, translucent body and vibrant blue underglaze, Chinese porcelain has been highly prized for centuries. The intricate designs often feature motifs symbolizing good fortune and prosperity. The art of Chinese porcelain has had a profound influence on ceramic art globally, inspiring countless imitations and adaptations.
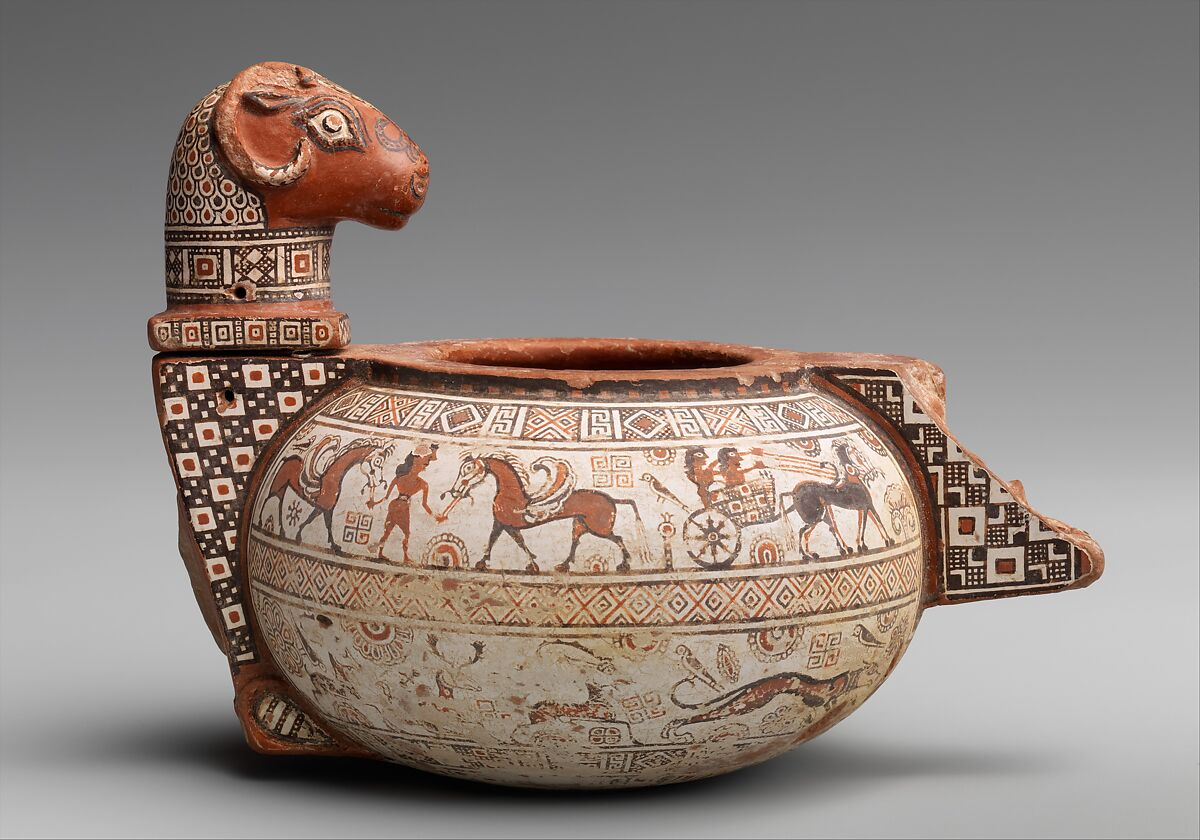
Native American Pottery
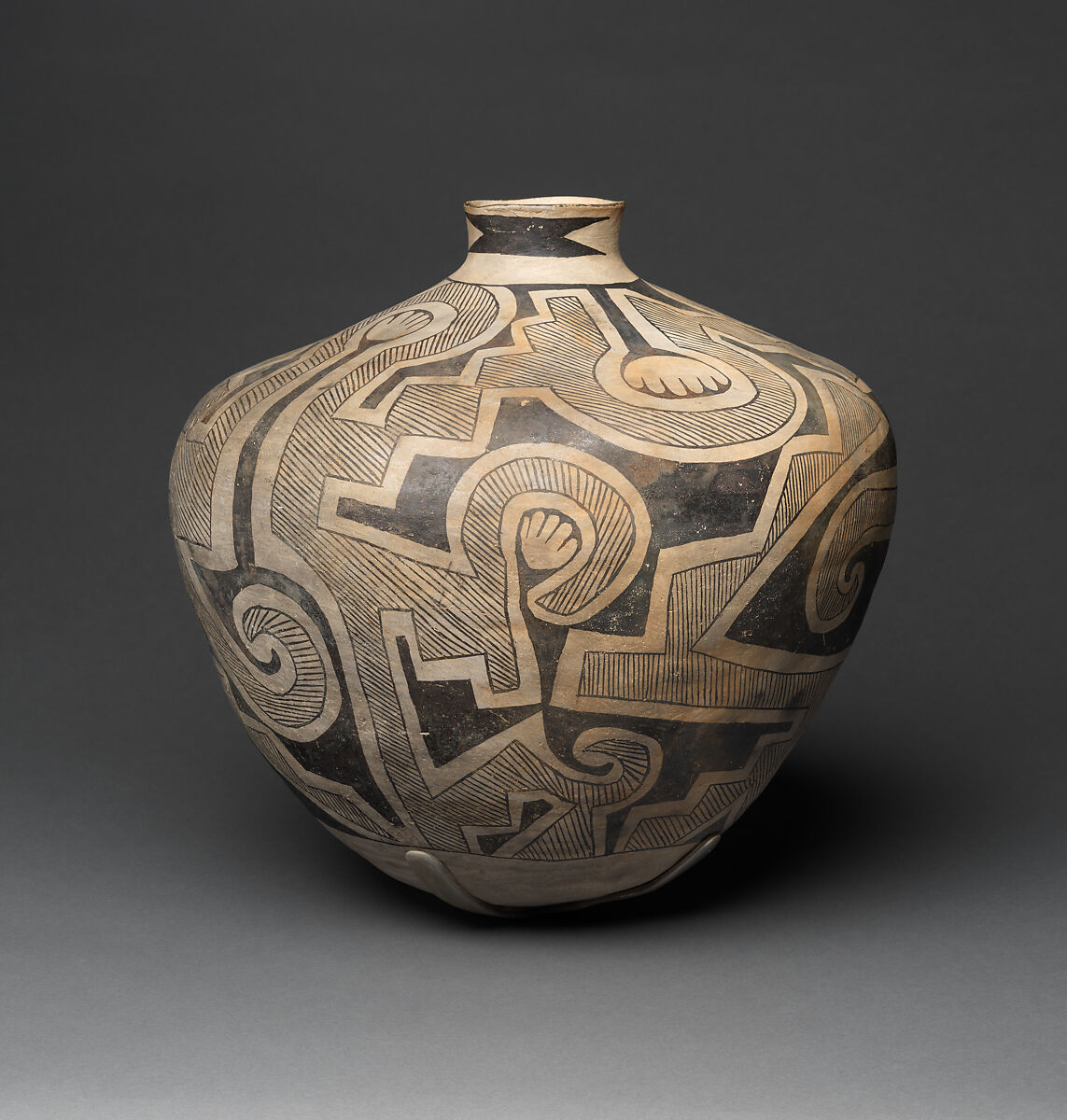


Socorro black-on-white storage jar, Ancestral Pueblo, Native American, ca. 1050–1100
Native American pottery, encompassing the work of numerous tribes across North America, varies widely in style and technique. Each tribe has developed its own distinctive pottery tradition, often passed down through generations.
These pottery styles range from the black-on-black pottery of the Southwest’s Pueblo peoples to the intricately carved designs of the Northwest Coast tribes. Techniques include coiling, pinching, and slab construction, with many pieces being traditionally fired in open pits or in kilns. The pottery often carries significant cultural symbolism, with designs and forms that are deeply rooted in the tribe’s history, mythology, and environment.
Prominent American Art Pottery Creators


Several American artists have made significant contributions to the field of art pottery, each bringing unique styles and techniques that have helped shape the medium. Some of the most respected American art pottery artists include the following.
George Ohr: Known as the “Mad Potter of Biloxi,” Ohr is celebrated for his innovative and eccentric pottery. His work is characterized by thin walls, twisted shapes, and vibrant glazes, which were ahead of his time.
Maria Martinez: A renowned Native American artist, Martinez is famous for her black-on-black pottery. She developed a unique style of Pueblo pottery, featuring matte designs on a glossy black background, and is credited with reviving this traditional art form.
Adelaide Alsop Robineau: A prominent figure in the Arts and Crafts Movement, Robineau is known for her exquisite porcelain pieces. Her most famous work, “Scarab Vase” or “The Apotheosis of the Toiler,” is considered a masterpiece of American pottery.
Grueby Faience Company and William Henry Grueby: Grueby founded the Grueby Faience Company in Boston, known for its distinctive matte green glazes and organic forms. Their work was instrumental in the American Arts and Crafts Movement.
Rookwood Pottery and Maria Longworth Nichols: Founded by Nichols, Rookwood Pottery is known for high-quality glazes and decorations, contributing significantly to the development of American art pottery.
Beatrice Wood: Wood was known for her lustrous, iridescent glazes and a whimsical approach to pottery. Her work, often in a luster glaze, shows a blend of modern and folk influences.
Toshiko Takaezu: An influential ceramicist, Takaezu’s work is noted for its closed forms, which turn functional pots into sculptural objects. Her approach to pottery was deeply spiritual and meditative.
Peter Voulkos: Voulkos played a significant role in moving pottery into the realm of large-scale sculpture. His work broke traditional boundaries, combining pottery and sculpture in innovative ways.
These artists represent just a fraction of the many talented individuals who have contributed to the rich and diverse history of American art pottery. Each artist brought a unique perspective and set of techniques to the medium. Each collection has helped to define and elevate pottery as a form of artistic expression.
Art Pottery in the Contemporary Scene
The contemporary art pottery scene is a vibrant and dynamic realm, reflecting both the rich traditions of the past and the innovative spirit of the modern world. Today’s art pottery world is marked by a diversity of styles and approaches, ranging from traditional techniques to avant-garde expressions.
There’s a growing appreciation for both handcrafted, artisanal pieces and experimental, contemporary works. The digital age has also introduced new ways for potters to share their work, learn new techniques, and connect with audiences globally. While mass-produced ceramics are widely available, there is a renewed interest in unique, handmade pottery that embodies individual artistic vision and skill.
Emerging Trends and Continuing Concerns in Contemporary Art Pottery
There’s an increasing focus on sustainable practices and materials in pottery, with artists exploring eco-friendly clays, glazes, and firing techniques. Many contemporary potters are blending traditional techniques with modern aesthetics, creating pieces that honor the past while embracing the present.
Experimentation with texture and form is prevalent, with artists pushing the boundaries of what can be achieved with clay. The use of 3D printing and digital design tools is becoming more common, allowing artists to explore complex forms and designs.
Contemporary pottery often carries narratives and personal stories, with artists using their work as a means of expression and communication.
Influence of Modern Artists and Global Cultural Exchanges on Contemporary Pottery
Contemporary art pottery is significantly influenced by the works of modern artists who challenge conventional notions of pottery. These artists often incorporate multidisciplinary elements and conceptual approaches, elevating pottery to the realm of fine art.
Global cultural exchanges have enriched the contemporary pottery scene, introducing a cross-pollination of styles and techniques. Artists are now more aware and influenced by pottery traditions from around the world, leading to a fusion of diverse aesthetic and cultural elements in their work.
The impact of international pottery exhibitions, residencies, and workshops has facilitated this exchange, creating a global community of potters who share, collaborate, and innovate. The contemporary scene of art pottery is a testament to the medium’s adaptability and enduring appeal. It continues to evolve, driven by artists who respect tradition yet are unafraid to experiment and innovate, making it a continually exciting and evolving field.
Final Thoughts on Art Pottery


Art pottery encompasses a rich and diverse history, marked by its evolution from functional utility to a medium of profound artistic expression. Tracing its roots back to ancient civilizations, art pottery has continuously adapted, reflecting cultural shifts and artistic innovations.
From the traditional elegance of Japanese raku and the intricate sophistication of Chinese porcelain to the bold expressions of the modern studio pottery movement, this art form has showcased the remarkable versatility and creativity of its practitioners.
Today, as it bridges the realms of traditional craftsmanship and contemporary artistic innovation, art pottery retains its enduring appeal, captivating both creators and admirers. Its place in the world of art is firmly established, not just as a testament to human creativity but as a medium that continually evolves, embracing new techniques and ideas while honoring its storied past.