Bioluminescent Lighting: Nature Illuminates the Built Environment
Summary
This article discusses the innovative use of bioluminescent lighting in architecture and design, showcasing how natural light-emitting organisms are being integrated into man-made fixtures. This approach offers eco-friendly lighting solutions, reducing energy use and environmental impact, while also providing unique aesthetic benefits.
Reflection Questions
- What are the potential environmental and aesthetic benefits of replacing traditional electric lighting with bioluminescent lighting in urban and domestic environments?
- Considering the technical and ethical challenges of maintaining living organisms for lighting, how might these be addressed to make bioluminescent lighting more feasible?
- How does the use of bioluminescent lighting reflect broader trends towards sustainability and natural integration in design?
Journal Prompt
Reflect on the integration of living organisms into everyday objects like lighting fixtures. Consider the ethical, environmental, and practical implications of using bioluminescent organisms. How do you feel about the balance between technological innovation and natural conservation in design? Explore your thoughts on where these practices might lead in the future of urban and interior design.
Bioluminescence, a phenomenon where living organisms produce light through a chemical reaction, has long intrigued scientists and laypersons alike. Primarily observed in marine species, such as certain types of fish, jellyfish, and microorganisms, bioluminescence occurs when light is emitted as a result of a biochemical reaction involving a light-emitting molecule and an enzyme. Recently, this natural occurrence has found novel applications beyond its biological origins, particularly in the fields of interior design, landscape architecture, and urban planning. The integration of bioluminescent plants and animals into man-made fixtures marks a burgeoning trend that merges natural luminescence with architectural aesthetics. This shift not only highlights the potential for sustainable lighting solutions but also opens new avenues for exploring the symbiosis between organic phenomena and human-centric design spaces. Read on to learn more about current and future applications of bioluminescent lighting.
The Science Behind Bioluminescence
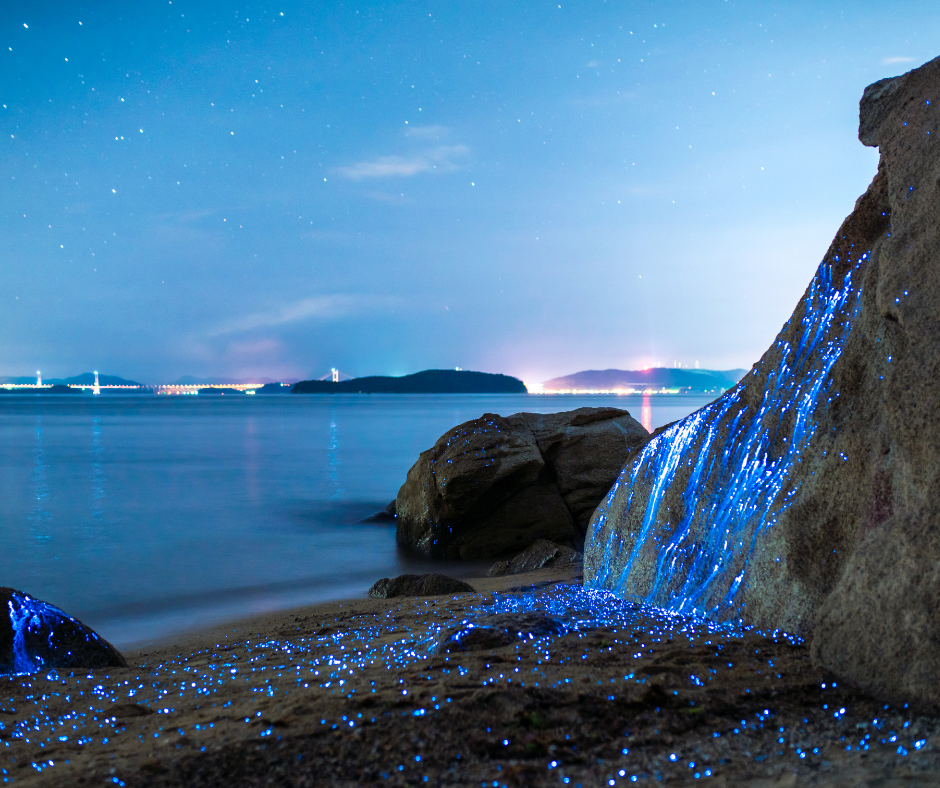


Bioluminescence results from a specific biochemical reaction, a process wherein certain organisms produce and emit light. This reaction primarily involves the enzyme luciferase, which acts on a substrate molecule, typically luciferin, in the presence of oxygen and adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The interaction triggers the oxidation of luciferin, producing light.
The color of the bioluminescent light, which ranges from green to blue and red, depends on the species and the structure of the luciferase and luciferin. However, most marine bioluminescence is a green-blue color. Red light emission is less common, but certain deep sea fish and deep sea squid do glow red. The efficiency of this light-producing reaction makes it a subject of interest in biochemistry, with potential applications extending into various scientific fields.
Species Exhibiting Bioluminescence
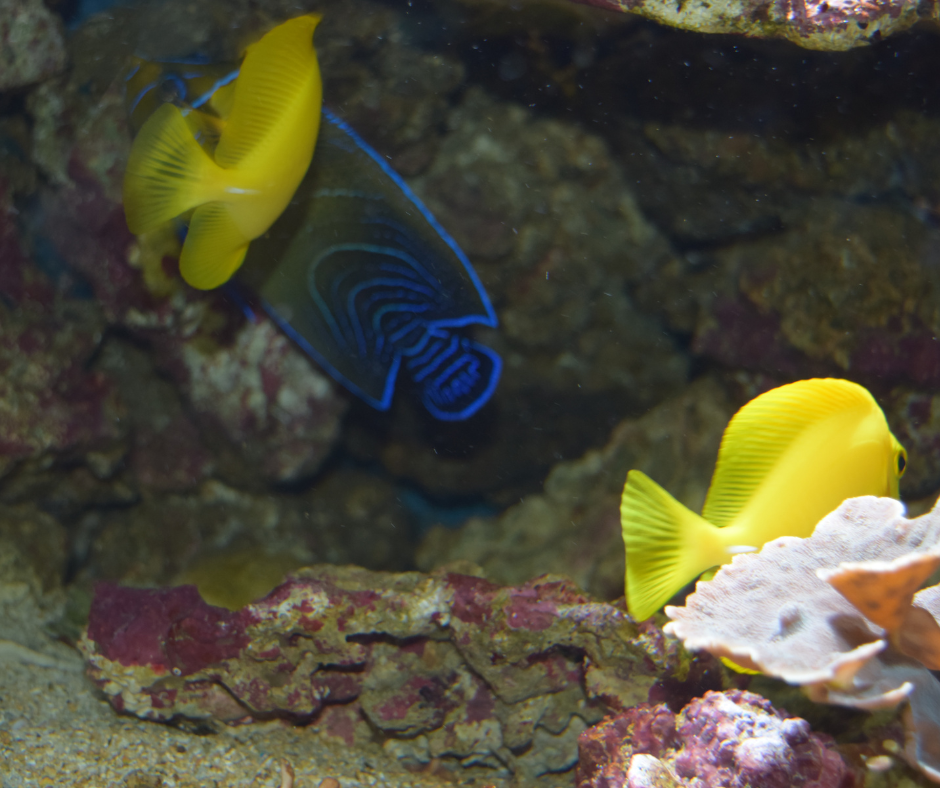


Various species, predominantly marine, exhibit bioluminescent properties. Notable among these are the fireflies (Lampyridae), known for their characteristic use of bioluminescence during twilight to attract mates. There are both bioluminescent animals and plants. In marine environments, the jellyfish (Aequorea victoria) and certain species of squid use bioluminescence as a defense mechanism, either to confuse predators or to illuminate and expose them to larger predators.
A deep sea organism, such as the anglerfish, produces light to attract prey. Another fascinating example is the bioluminescent plankton, like dinoflagellates, which cause the ocean to glow through chemical reactions and are often observed in warmer coastal waters. With their light-producing organs, these species demonstrate the diverse functional roles that bioluminescence plays in the natural world.
Historical Context and Cultural Significance of Bioluminescence
Throughout history, animals, fungi, and plants that produce bioluminescence have fascinated and influenced various cultures, often shrouded in myth and mystery. Ancient civilizations, such as the Greeks and Romans, documented bioluminescent phenomena, particularly in marine life, viewing it as a manifestation of divine or supernatural power. In the early scientific writings, luminous organisms were described with a mix of curiosity and speculative lore.
During the Age of Exploration, sailors and explorers recounted eerie glows in the ocean, often attributing them to mythical creatures or omens. These historical accounts reflect not only the intrigue and wonder surrounding bioluminescence but also the limited understanding of its biological underpinnings until modern scientific advancements.
Symbolism in Various Cultures
In various cultures, bioluminescence holds significant symbolic meaning, often intertwined with folklore and spiritual beliefs. For instance, in Japanese folklore, fireflies are seen as sacred and symbolic of passionate love, partly due to their fleeting and ephemeral light.
Similarly, in some Native American cultures, fireflies represent the souls of the departed, guiding the living with their gentle light. In Caribbean folklore, the mystical glow of certain marine organisms is often connected to sea spirits and guardians of the ocean.
These cultural interpretations of bioluminescence underscore its impact beyond scientific interest, enriching local folklore and spiritual symbolism across different societies.
Bioluminescent Lighting in Interior Design, Landscape Architecture, and Urban Planning
Bioluminescence is increasingly being adopted in modern interior design and urban planning as an innovative and sustainable lighting solution. In interior design, bioluminescent organisms are used in features like living walls and decorative installations, providing a dynamic and organic light source. For example, bioluminescent algae in sealed glass installations offer a sustainable and low-energy alternative for ambient lighting.
In urban planning, initiatives like the project in Rambouillet, France, experiment with bioluminescent bacteria for street lighting, aiming to reduce energy consumption and environmental impact. These applications represent a shift towards integrating natural, living elements in design, highlighting the potential for bioluminescent technology to transform our living and communal spaces.
Design Techniques and Aesthetics
Designers incorporate bioluminescence into interiors and urban spaces using a variety of techniques that emphasize both functionality and aesthetic appeal. Techniques include encapsulating bioluminescent organisms in transparent, durable materials to create lighting fixtures or embedding them into architectural elements like walls or paths.
Aesthetically, bioluminescence offers a unique visual experience, characterized by its gentle, ethereal glow. This natural light source provides a calming and immersive atmosphere, often used in spaces designed for relaxation or contemplation.
The color and intensity of the light can vary depending on the organism used, allowing for creative and bespoke design solutions. The use of bioluminescence in design not only pushes the boundaries of traditional lighting but also adds a new dimension to the sensory experience of a space.
Sustainability and Environmental Benefits
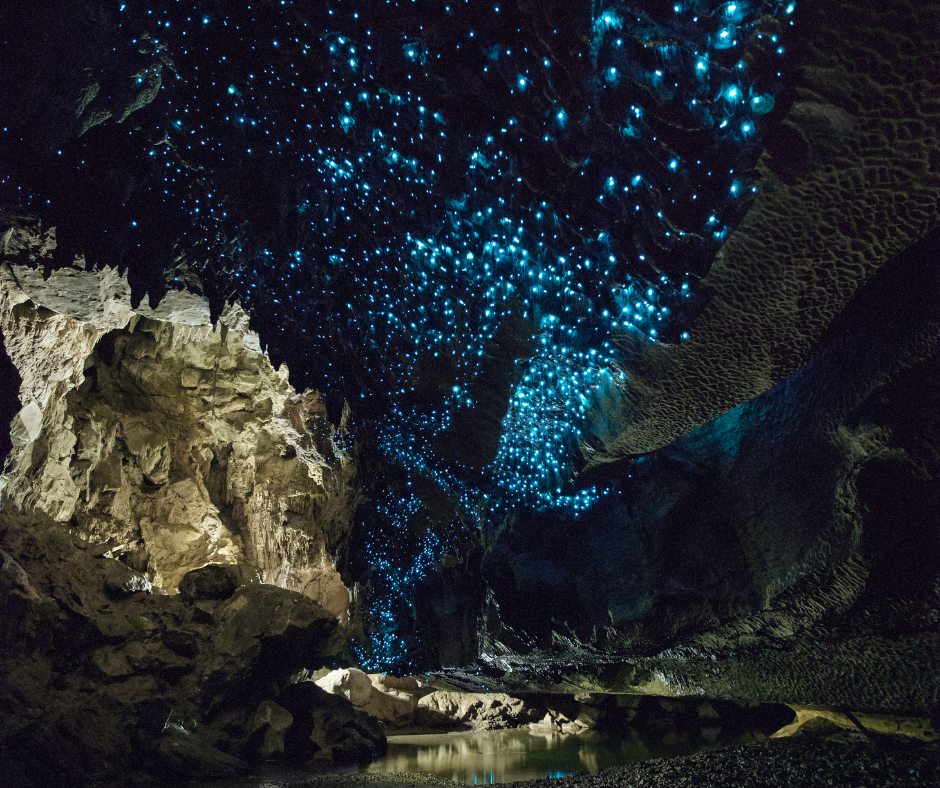


The utilization of bioluminescent lighting presents notable environmental advantages over conventional lighting methods. Bioluminescent light sources, deriving from natural organisms, require no electrical power, significantly reducing energy consumption and carbon emissions associated with traditional lighting. This method of illumination circumvents the need for fossil fuels, contributing to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions.
Furthermore, bioluminescent lighting minimizes light pollution, a growing concern in urban environments, due to its inherent soft and natural glow. These features position bioluminescence as a promising eco-friendly alternative, aligning with global efforts to mitigate environmental impact and embrace sustainable practices.
Renewable and Sustainable Practices
Bioluminescent lighting exemplifies a sustainable approach to illumination, with long-term prospects for renewable use. The self-replenishing nature of biological light sources, under optimal conditions, offers a continual cycle of illumination without depleting resources. Efforts to cultivate bioluminescent organisms in controlled environments could lead to sustainable and renewable production methods.
The challenge lies in developing efficient systems for maintaining and nurturing these organisms to ensure consistent and long-lasting light output. Advances in biotechnology and sustainable design are crucial to fully realize the potential of bioluminescent lighting as a viable, long-term alternative to conventional lighting solutions.
Challenges and Limitations of Using Light Emitted by Plants, Fungi, and Bacteria
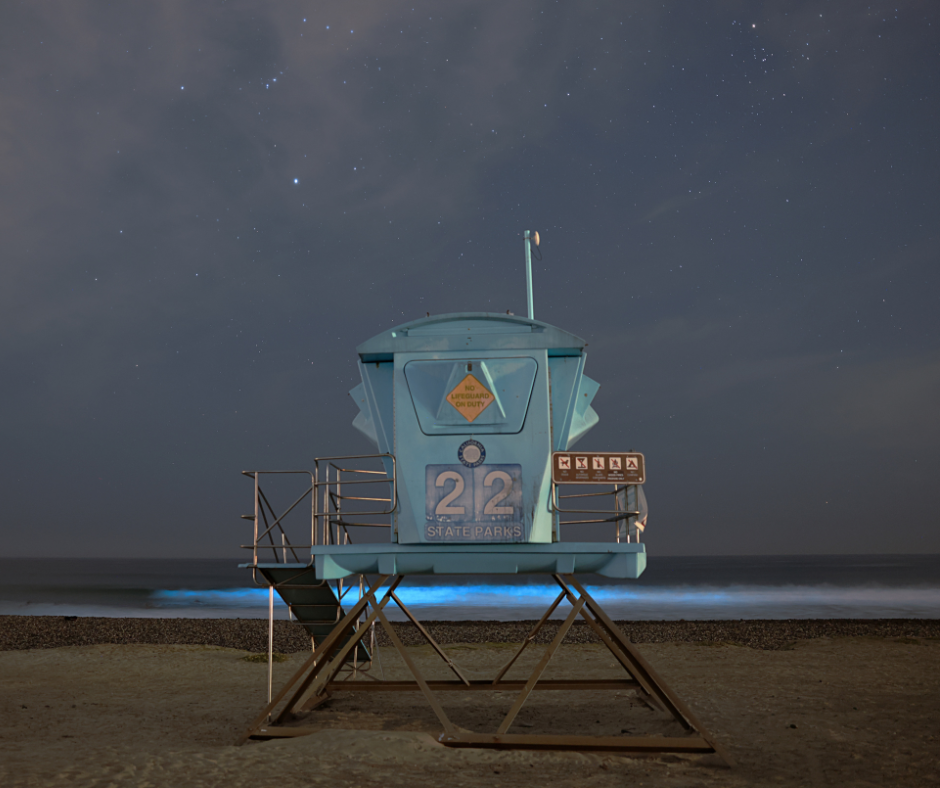


Harnessing bioluminescence for practical use in interior settings presents several technical challenges. One primary concern is the longevity and stability of the light output. Bioluminescent organisms require specific environmental conditions to thrive and produce light consistently. Maintaining these conditions, such as the right temperature, nutrient balance, and oxygen levels, can be complex and resource-intensive.
Additionally, the intensity of the light produced by these organisms is generally lower compared to traditional artificial lighting, which may limit their applicability in certain settings. Furthermore, the integration of living organisms into functional design elements necessitates careful consideration of ethical and biological factors, ensuring the well-being of the organisms while meeting design objectives.
accepting new mastermind applications
For Fall ’24
Get unstuck. Find fulfillment. Rediscover your passion for the design industry we all love! Be one of the first to join our next exclusive, curated cohort of creative women and find support like you’ve never had before.


Current Limitations and Future Possibilities
Currently, the limitations of bioluminescent lighting technology include its relatively low luminosity and the logistical challenges of maintaining living light sources over extended periods. These constraints restrict the scalability and widespread adoption of bioluminescent lighting solutions. However, ongoing research and technological advancements hold promise for the future.
Potential developments include enhancing the brightness and longevity of bioluminescent light, as well as engineering more robust and adaptable bioluminescent organisms. Innovations in biotechnology could lead to more efficient and sustainable methods of cultivating and utilizing these organisms, expanding the practical applications of bioluminescent lighting in various contexts.
As research progresses, bioluminescent lighting has the potential to become a more viable and versatile option in the realm of sustainable and eco-friendly design.
Case Studies: Bioluminescent Lighting in Action
Teresa van Dongen’s Ambio Lamp
Teresa van Dongen, before embarking on her career as a designer, studied biology for two years. During her studies in biology, she discovered that nature and international science labs focusing on nature are full of wonders that remain relatively unknown to the wider public. This early exposure to biology and the natural world played a significant role in shaping her approach to design, particularly her interest in integrating natural elements and phenomena, such as bioluminescence, into her work.
This unique blend of scientific understanding and design innovation is evident in her creations, such as the Ambio lamp, which uses bioluminescent bacteria to produce light. As Liz Stinson writes in this article for Wired, “The Dutch designer created the Ambio for her graduation project at Eindhoven’s Design Academy” nearly a decade ago.
Teresa van Dongen’s Ambio lamp is a unique bioluminescent lighting design that harnesses the natural light-emitting capabilities of bacteria. These bacteria, often found in the sea, emit light when mixed with oxygen in the water. The Ambio lamp, designed to swing gently, utilizes this natural phenomenon, allowing the bacteria to light up as the lamp moves, creating a sustainable and visually stunning light source.
However, the bacteria currently survive and emit that gentle blue-green light only for a short period, with ongoing research to extend their lifespan for practical use in everyday life. Van Dongen’s work symbolizes the potential of using bioluminescent organisms to create light more sustainably.
The Streetlights of Rambouillet
In Rambouillet, France, a remarkable project is underway to use bioluminescent bacteria as an alternative to traditional street lighting. This innovative approach is a collaboration between the town and the start-up company Glowee. The project aims to create a unique ambiance in the streets, offering a sustainable and energy-efficient lighting solution.
The bioluminescent lighting is achieved by storing a marine bacterium, known as Aliivibrio fischeri, in saltwater-filled tubes. These bacteria emit a gentle blue light, providing illumination to the streets. This method of lighting is not only energy-efficient but also adds a unique aesthetic to the urban environment. Marine bioluminescence requires oxygen to create light, so the lighting system includes a small mechanism that circulates oxygen into the tanks.
This initiative is part of a larger movement towards sustainable and environmentally friendly urban solutions. The use of bioluminescent bacteria for street lighting is still in the experimental phase, with ongoing efforts to improve the technology and make it more practical for widespread use. As of now, the light these bioluminescent organisms produce is less intense compared to traditional lighting methods, but the project represents a significant step towards innovative, eco-friendly urban lighting solutions.
This project in Rambouillet demonstrates the potential of biotechnology to reshape our approach to urban design and sustainability, offering a glimpse into the future of public lighting.
Fuel your creative fire & be a part of a supportive community that values how you love to live.
subscribe to our newsletter
*please check your Spam folder for the latest DesignDash Magazine issue immediately after subscription


The Future of Bioluminescent Lighting in Architecture
Emerging Trends and Innovations
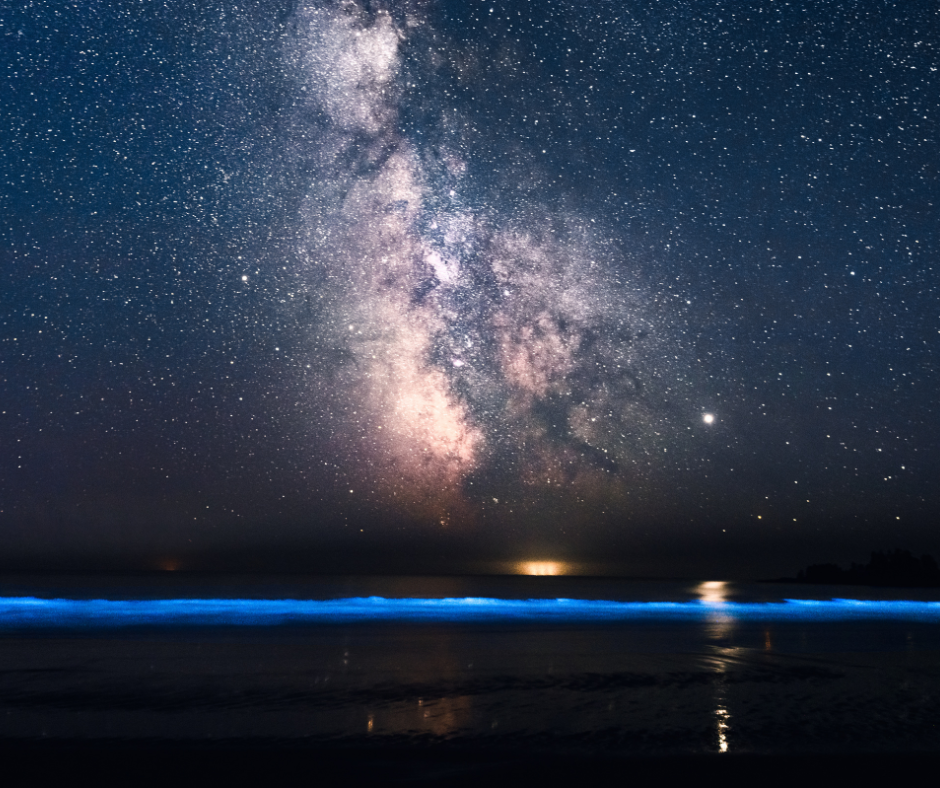


The future of bioluminescent lighting in interior design is poised to be shaped by emerging trends and innovations. Advancements in biotechnology are expected to enhance the viability and efficiency of bioluminescent lighting, making it a more practical option for widespread use.
Innovations may include the development of genetically modified organisms with increased luminosity and longevity, as well as the creation of hybrid systems that combine bioluminescent elements with traditional lighting for more versatile applications. Additionally, the integration of smart technologies could allow for greater control and customization of bioluminescent lighting, adapting to different environments and user needs.
These advancements will likely drive a new wave of eco-friendly and energy-efficient design, reflecting a growing emphasis on sustainability and natural aesthetics in interior design.
Potential Impact on Architecture and Design
Bioluminescent lighting holds the potential to significantly transform future architectural and design practices. As a sustainable and energy-efficient light source, it aligns with the increasing focus on green building and eco-conscious design principles.
Bioluminescent lighting could lead to new design paradigms where living light sources are seamlessly integrated into architectural elements, blurring the lines between nature and built environments. This approach could inspire innovative architectural designs that prioritize environmental harmony and user well-being.
Moreover, the unique aesthetic qualities of bioluminescent lighting offer architects and designers novel ways to enhance the ambiance and experiential aspects of spaces. Overall, the incorporation of bioluminescent lighting into architecture and design could herald a shift towards more organic, sustainable, and user-centered design approaches.
Final Thoughts on Bioluminescence in the Built Environment
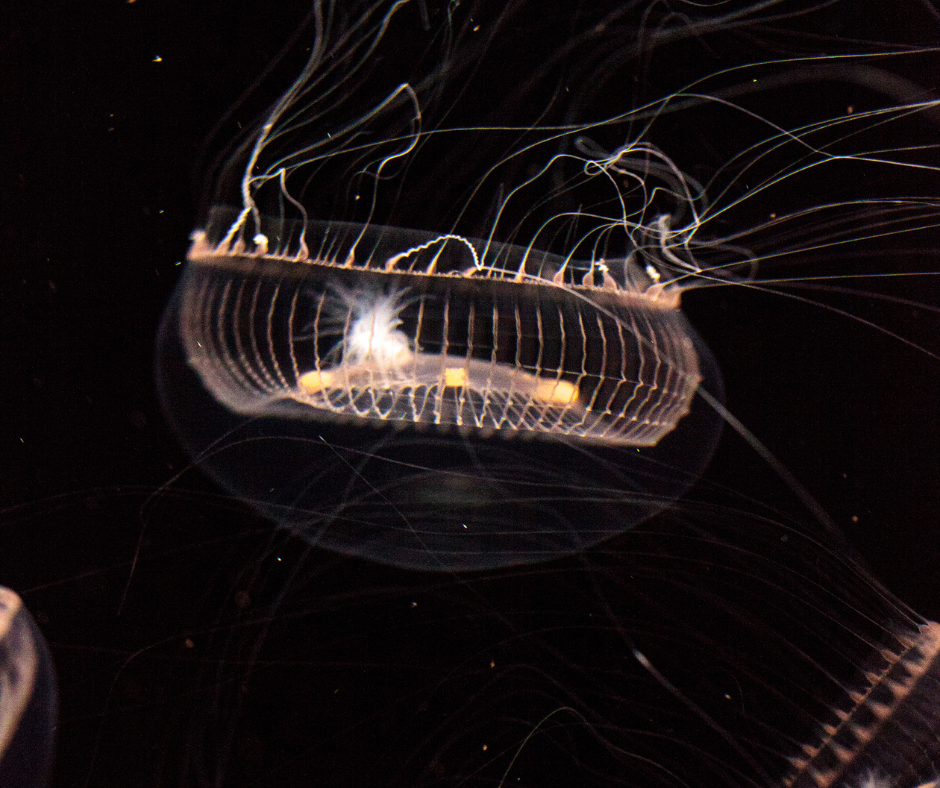


Our exploration of bioluminescent lighting underscores a growing trend in design that marries the intrinsic beauty of natural phenomena with human ingenuity. The seamless integration of bioluminescence into man-made environments not only highlights nature’s inherent aesthetics but also brings forth a sustainable approach to lighting and design.
As we look toward the future, the potential of bioluminescence in interior design appears promising, offering avenues for innovation, sustainability, and a deeper connection between our living spaces and the natural world. This confluence of biology and design opens up exciting possibilities for eco-friendly and energy-efficient solutions, reshaping how we think about and interact with our built environments.
The continued exploration and development of bioluminescent lighting technology will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in the evolution of design practices, emphasizing harmony with nature and a commitment to sustainability.