Hardening Homes with Fire-Resistant Building Materials
Summary
Reflection Questions
Journal Prompt
As wildfires worsen both nationwide and globally, the need for fire-resistant building materials has never been greater. Despite efforts to mitigate wildfire risk across the country, the frequency and severity of fires continue to increase, driven by climate change, human activity, invasive plant species, and other factors. To better protect homes and neighborhoods, we must adopt fire-resistant building materials and smart landscaping practices that can help delay fire damage until firefighters arrive. Below is our list of traditional, modern, and emerging fire resistant building materials designed to protect homes and their residents.
Worsening Wildfires Nationwide and Abroad
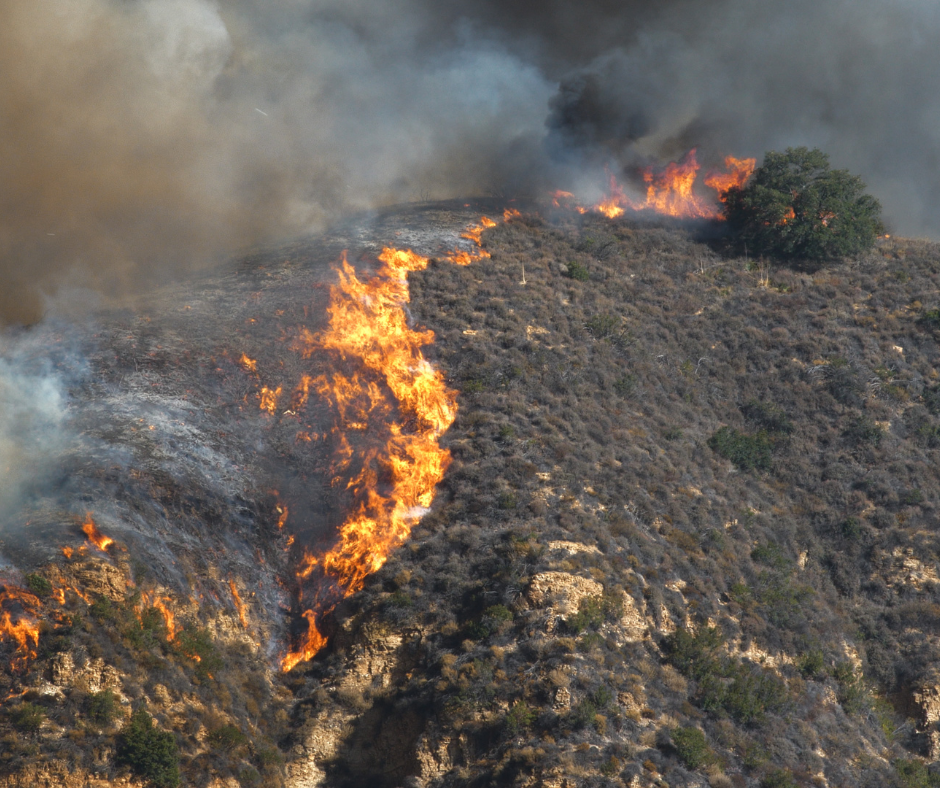


According to this resource from the EPA, “The wildfire season has lengthened in many areas due to factors including warmer springs, longer summer dry seasons, and drier soils and vegetation.” Several states in the United States are particularly prone to wildfires due to their climates, vegetation, and other environmental factors. In the Western region, California, Oregon, Washington, Colorado, Arizona, and Nevada are highly susceptible to wildfires. These states experience hot, dry summers, and their landscapes are filled with dense forests, grasslands, and chaparral that provide ample fuel for fires.
Other states like Idaho and Montana, with their dry summers and cold winters, also face considerable wildfire threats, highlighted by fires like Idaho’s Pioneer Fire (2016) and Montana’s Rice Ridge Fire (2017). Efforts to mitigate wildfire risk across these regions include improved forest management practices, public education on fire prevention, and enhanced emergency response systems.
Still, fires are becoming more common and severe in many parts of the world. Several factors contribute to this increase.
Climate Change
Rising global temperatures lead to longer and more intense fire seasons. Prolonged dry periods make vegetation more flammable, and higher temperatures can lead to more thunderstorms, which can ignite fires.
Human Activity


As more people move into wildland areas (the wildland-urban interface), the risk of fires increases. Slash-and-burn agriculture and other land management practices can contribute to wildfires, and human activities like campfires and discarded cigarettes can start fires.
Forest Management Practices
Decades of fire suppression have led to the accumulation of dry fuel in forests, making fires more severe when they do occur. Some logging practices can leave behind highly flammable debris.
Invasive Species


Invasive plant species can increase the flammability of certain areas by introducing vegetation that burns more easily and rapidly than native plants. These invasive species often grow quickly, creating dense and continuous fuel loads that can easily ignite and spread fire.
Additionally, some invasive plants, like certain grasses and shrubs, produce dry, fine materials that are particularly prone to catching fire. This change in the vegetation landscape disrupts the natural fire regimes and makes it more difficult to manage and control wildfires, ultimately increasing the frequency and intensity of fires in affected regions.
How Designers and Homeowners Improve the Fire Resistance of Residential Properties


Choosing fire-resistant or fireproof building materials for your home’s construction and landscaping can significantly reduce the risk of fire damage. For instance, using fire resistant material like metal, clay tiles, or asphalt shingles rated for fire resistance can help protect the roof from igniting during a wildfire.
Additionally, opting for non-combustible siding materials like fiber-cement board, stucco, brick, or stone can further safeguard the structure. Installing fire resistant windows that either have double-pane or tempered glass can withstand high temperatures and prevent heat from entering the home.
Similarly, opt for fire rated doors. Solid-core or metal doors are less likely to catch fire compared to hollow-core wood doors. Constructing decks and patios with fire-resistant materials like composite decking, metal, or concrete also adds an extra layer of protection.
Landscaping to Create a Fire Resistant Barrier


Landscaping plays a crucial role in wildfire protection as well. Creating a defensible space around your home by clearing away flammable vegetation and debris is essential. Maintaining a zone of at least 30 feet with fire-resistant plants and materials can help prevent a fire from reaching your home.
Choosing plants that are less likely to ignite, like those with high moisture content, and spacing them appropriately can further reduce the risk of fire spread. Using non-combustible mulch materials like gravel or stone instead of wood chips or bark is another effective measure to enhance fire safety.
Additional measures to protect your home from wildfires include keeping gutters clear of leaves and debris and installing ember-resistant vent covers to prevent embers from entering the home. Establishing fire breaks by clearing vegetation along property lines and around structures can also be beneficial. Ensuring that driveways and roads are accessible to emergency vehicles and clearly marked is crucial for emergency response.
Traditional, Modern, and Emerging Fire-Resistant Building Materials to Harden Your Home


Protecting your home and neighborhood from wildfires is a critical concern, especially in areas prone to such natural disasters. By strategically selecting from a variety of traditional, modern, and emerging fire-resistant building materials and implementing smart landscaping practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of fire damage.
These materials might not completely prevent your home from suffering damage, but they can provide crucial protection, potentially delaying the fire’s progress until firefighters arrive. Utilizing materials that are less likely to ignite and creating defensible spaces around your property can provide a robust line of defense against the devastating effects of wildfires.
Traditional Fire-Resistant Materials
Brick and Mortar


First on our list of traditional fire retardant materials is brick and mortar. Brick is a naturally non-combustible material that can withstand high temperatures without igniting or emitting toxic gases. This makes it an excellent choice for building walls and structures that need to endure intense heat.
Mortar, which is made from a mixture of sand, cement, and lime, holds the bricks together and shares similar non-combustible properties. Together, brick and mortar provide a durable and fire-resistant building solution that has been used for centuries.
Concrete
Concrete is another highly effective fire-resistant material, particularly in its reinforced form. Reinforced concrete combines concrete with steel reinforcement, which enhances its structural integrity and fire resistance. This makes it ideal for constructing buildings and infrastructure that need to maintain their strength during a fire. Additionally, aerated concrete is a lightweight variant that offers excellent thermal insulation and fire resistance, making it suitable for various construction applications.
Stucco


Stucco is a plaster made from cement, sand, and lime that is applied over walls and surfaces to create a fire-resistant coating. This traditional material not only provides a durable and weather-resistant finish but also adds an extra layer of protection against fire. Stucco is commonly used in both residential and commercial buildings to enhance their fire resistance and overall durability.
Stone
Natural stones like granite and limestone are inherently non-combustible and highly fire-resistant. These materials have been used in construction for centuries due to their ability to withstand extreme temperatures without degrading. Stone is often used in building facades, fireplaces, and other structural elements to provide both aesthetic appeal and robust fire protection.
Gypsum Board (Drywall)


Next on our list of fire retardant building materials is drywall. Gypsum board, commonly known as drywall, is composed of a non-combustible core of gypsum. It is widely used in interior walls and ceilings for its excellent fire-resistant properties. When exposed to fire, gypsum board helps to slow down the spread of flames and provides critical time for evacuation and firefighting efforts.
Gypsum slows down the spread of flames through its non-combustible nature and its ability to release water vapor when heated. The core of gypsum board contains chemically bound water molecules, and when exposed to high temperatures, this water is released as steam. This process, known as calcination, absorbs heat and helps to cool the surrounding area, effectively slowing down the fire’s progress and reducing the spread of flames.
The gypsum itself also acts as a thermal barrier, providing further resistance to fire penetration. This makes it a staple material in modern construction for enhancing the fire safety of buildings.
Fuel your creative fire & be a part of a supportive community that values how you love to live.
subscribe to our newsletter
*please check your Spam folder for the latest DesignDash Magazine issue immediately after subscription


Modern Fire-Resistant Materials
Intumescent Coatings
Intumescent coatings are innovative, paint-like substances that significantly enhance fire resistance. When exposed to high temperatures, these coatings swell and form a thick, insulating barrier. This expanded layer protects the underlying material by slowing the rate at which heat is transferred, thereby delaying the spread of flames and giving additional time for evacuation and firefighting efforts.
Glass-Fiber Reinforced Gypsum (GFRG)
Glass-Fiber Reinforced Gypsum, or GFRG, combines gypsum with fiberglass to create a material that is both strong and lightweight, while also being highly fire-resistant. This modern material is commonly used in walls and ceilings, providing enhanced fire protection in addition to structural support. GFRG’s resistance to high temperatures makes it an ideal choice for improving the overall fire safety of buildings.
Fire-Resistant Glass Windows


Fire-resistant glass, including types like tempered or laminated glass, is designed to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of flames. These specialized glass materials can endure the intense heat of a fire without breaking or allowing the fire to penetrate through them. This makes fire-resistant glass an essential component in windows, doors, and other architectural elements where both transparency and safety are required.
Fiber Cement Board
Fiber cement board is made from a mixture of cement, sand, and cellulose fibers, creating a durable and fire-resistant material. It is commonly used for siding, roofing, and other building applications where both strength and fire protection are needed. Its composition allows it to withstand high temperatures without combusting, thus providing a reliable barrier against the spread of fire.
Industrial Metals
Next, consider steel and aluminum. Steel is inherently fire-resistant and is widely used in structural frameworks due to its strength and durability. When coated with fireproofing materials, its resistance to heat is further enhanced, making it an excellent choice for supporting large structures and maintaining integrity during a fire.
Often used as a fire resistant roofing material and in cladding, aluminum can withstand high temperatures, but it can lose strength when exposed to extreme heat for prolonged periods. It provides a lightweight, durable option for protecting buildings from fire but is typically used with other fire-resistant measures.
Fire-Retardant Treated Wood


Fire-retardant treated wood is wood that has been chemically treated to enhance its resistance to fire. This treatment makes the wood less likely to ignite and slows the spread of flames, making it suitable for framing and structural components. It allows builders to use the aesthetic and structural benefits of wood while significantly reducing fire risks.
Mineral Wool Insulation
Mineral wool insulation, made from natural rock or slag, offers excellent fire resistance and is commonly used for insulating walls, roofs, and floors. This fire resistant insulation has non-combustible properties that make it an ideal choice for improving the fire safety of buildings by providing thermal insulation that can withstand high temperatures without burning.
Ceramic Tiles


Ceramic tiles are non-combustible and highly heat-resistant, making them an excellent choice for use in floors, walls, and countertops. Their ability to endure high temperatures without damage or ignition adds a layer of fire protection to surfaces, making them suitable for both residential and commercial applications.
Geopolymer Concrete
Geopolymer concrete is an innovative material made from industrial waste products like fly ash, offering superior fire resistance compared to traditional concrete. This environmentally friendly material not only provides excellent structural integrity but also significantly improves fire protection, making it an attractive option for modern construction.
Autoclaved Aerated Concrete (AAC)
Autoclaved Aerated Concrete (AAC) is a lightweight, precast concrete material that is highly fire-resistant and offers excellent thermal insulation. Its porous structure allows it to withstand high temperatures, making it an effective barrier against fire while also providing energy efficiency benefits. AAC is widely used in both residential and commercial building projects.
Emerging Fire-Resistant Materials
Nanomaterials
Nanomaterials indeed enhance the fire resistance of traditional materials through the incorporation of nanotechnology. These extremely fire resistant materials, like carbon nanotubes and nanoclays, can improve thermal stability and reduce flammability. They work by creating a protective layer that can insulate and prevent the spread of fire. Research and development in this area are ongoing, with promising results for future applications in building materials.
Phase Change Materials (PCMs)
Phase Change Materials (PCMs) are integrated into building materials to help regulate temperature and enhance fire resistance. They absorb and release large amounts of heat during phase transitions (e.g., from solid to liquid), which can help manage heat loads in buildings. This characteristic helps slow down the rise in temperature and can provide a cooling effect that contributes to fire resistance. PCMs are being explored for use in various construction materials, including insulation and wallboards.
High-Performance Polymers
High-performance polymers are advanced materials designed to withstand high temperatures and resist flame spread. These polymers, like certain high-performance thermoplastics and thermosets, maintain their structural integrity under extreme heat conditions.
They are used in coatings, insulation, and structural components to enhance fire resistance. These materials are being continuously developed to improve their fire-resistant properties and are already used in some specialized construction applications.
Final Thoughts on Wildfire Hardening


By incorporating traditional materials like brick, concrete, and stucco, along with modern innovations like intumescent coatings, fiber cement board, and fire-resistant glass, homes can be better protected against the devastating effects of fire. Emerging technologies like nanomaterials and phase change materials offer even greater levels of fire resistance.
Beyond building materials, pursuing other hardening methods like creating defensible spaces through appropriate landscaping, maintaining clean gutters, installing ember-resistant vent covers, and establishing fire breaks can further enhance the safety of properties. Educating communities about fire prevention and preparedness is also vital. By taking these comprehensive measures, we can significantly reduce the risk of fire damage and safeguard our homes and neighborhoods against wildfires.