Masdar City: All about the 22 Billion Dollar Sustainable Eco City
Summary
This article provides an in-depth look at Masdar City, a $22 billion sustainable eco-city project in Abu Dhabi. It highlights the city’s innovative design, which incorporates renewable energy, sustainable architecture, and advanced technology to minimize environmental impact. The piece discusses the goals of Masdar City, its current status, and the challenges it faces, offering insights into the future of urban development and sustainability.
Reflection Questions
- How can the principles of sustainable design and renewable energy used in Masdar City be applied to your own projects or business practices?
- What are the potential benefits and challenges of integrating advanced technology and sustainable practices into your work?
- How does the concept of creating a sustainable and eco-friendly environment resonate with your values and long-term vision as a creative entrepreneur?
Journal Prompt
Reflect on the concept of sustainability and how it applies to your creative work and business. Write about ways you can incorporate sustainable practices into your projects, whether through materials, design choices, or energy use. Consider the impact these changes could have on your business, clients, and the broader community, and outline a plan for implementing sustainable practices in your work.
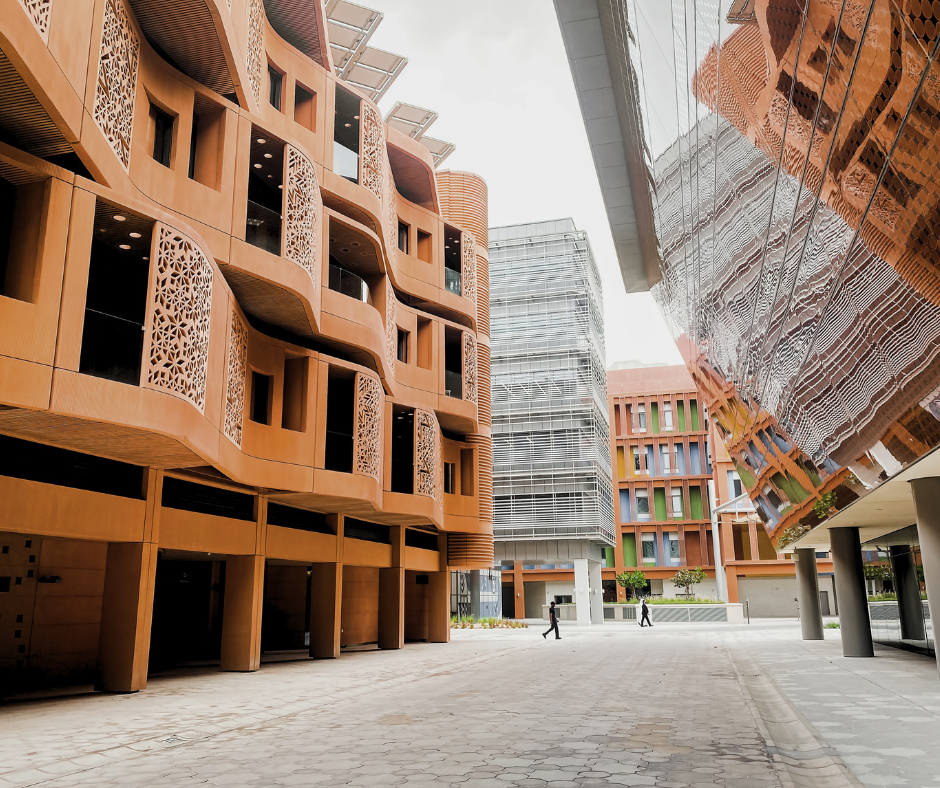
Masdar City—planned in Abu Dhabi, UAE near the Abu Dhabi International Airport—will be a pioneering urban development project initiated by a subsidiary of the Mubadala Development Company. Upon completion, this ambitious project will be one of the world’s most sustainable urban communities. Still, its initiatives will significantly reduce the area’s environmental impact and promote the adoption of renewable energy technologies across the UAE. Masdar City planners will integrate advanced architectural design, cutting-edge renewable energy systems, and comprehensive sustainability practices. By combining these principles, Masdar should be a model for future cities worldwide. However, the city is not without challenges—including environmental issues, financial barriers, and criticisms as to whether it is ever truly sustainable to build a city in the desert. Is Masdar City a cautionary tale of grand expectations that fall short in the face of real-world challenges, or a beacon of hope for a global community struggling to limit its impact on the natural environment? Read on to learn more.
Masdar City: Design and Architecture in Abu Dhabi

Masdar City is expected to emerge as a global leader in renewable energy and sustainable living upon completion. While not quite the diverse hub promised by its designers and investors, the city is definitely on its way with plans to keep growing and evolving into the 2030s. Right now, it’s more of a hub for businesses and research than a bustling city full of residents.
While some have dubbed Masdar City a “failed” project for missing so many deadlines, there is still a grand vision underlying it all. The famous British architecture firm Foster + Partners designed Masdar City with sustainability and innovation in mind. They took inspiration from traditional Arab cities, incorporating narrow streets and shaded walkways to create cooler microclimates—a smart move in the scorching Abu Dhabi desert.
Put simply, Masdar City’s developers want to create a compact, mixed-use community that’s easy on the environment. By thinking carefully about the layout and the materials used, Masdar City hopes to minimize its energy consumption while making life more comfortable in the heat. While it’s still a work in progress, Masdar City is definitely a project to watch as it continues to push the boundaries of sustainable urban design.
Let’s take a closer look at how Foster + Partners designed Masdar City to accomplish these goals.
Exploring the Original Urban Layout of Masdar City

Its planners designed Masdar City’s urban layout to prioritize pedestrian movement and reduce reliance on automobiles. The compact design features narrow, shaded streets that encourage walking and cycling. Public spaces, parks, and plazas will be integrated throughout the city to promote social interaction and community engagement beyond the home.
Such a layout not only minimizes the environmental impact of Masdar but also creates a more livable, human-scaled urban environment. The design facilitates efficient public transportation options—including the Personal Rapid Transit (PRT) system pictured above. This further reduces the carbon footprint of its future residents.
Energy-Efficient and Net Zero Energy Buildings
The buildings in Masdar City are and will continue to be constructed using energy-efficient materials and innovative design techniques to maximize natural light and ventilation while minimizing heat gain. Such designs incorporate high thermal mass materials and advanced insulation to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures and reduce energy consumption for cooling.
Masdar City architects have designed the facades of each building to minimize dust accumulation and facilitate easy maintenance in the harsh desert climate. (However, dust and sand will continue to cause issues with the city’s energy system.) The buildings boast photovoltaic panels and other renewable energy features that generate their own power.
Let’s take a closer look at some of the individual buildings in Masdar City and their unique designs.
Masdar Institute of Science and Technology
Now part of Khalifa University, this research institution focuses on renewable energy and sustainability. The campus itself is a model of sustainable design in that it boasts energy-efficient buildings, smart water management systems, and facilities for advanced research.
Siemens Middle East Headquarters
Completed in 2014, this building is a prime example of sustainable office design. It incorporates energy-efficient lighting, advanced cooling systems, and a facade designed to minimize heat gain. The Siemens headquarters was awarded a LEED Platinum certification, which reflects its designers’ high standards in sustainable construction.
Estidama Mosque
The first mosque in Masdar City, Estidama also adheres to the highest sustainability standards—including LEED Platinum certification. Designed to use nearly 50% less energy than conventional houses of worship, visitors will find skylights, traditional Arabic screens, and high-performance insulation within the mosque.
International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) Headquarters
Serving as the global headquarters for IRENA, this building integrates various sustainable features like energy-efficient systems, renewable energy technologies, and environmentally friendly materials.
Net-Zero Energy Buildings
Masdar City has several net-zero energy projects, including NZ1, the UAE’s first net-zero energy commercial building, and the upcoming Masdar City Square, which includes a cluster of seven sustainable buildings. In fact, Masdar City intends the entire city to be net-zero.
Masdar City’s Sustainability Features
Primarily powered by solar energy, Masdar City is a pioneering model of renewable energy utilization. It follows the Estidama Pearl Rating System, which is a green building certification developed by the Abu Dhabi Urban Planning Council. At the heart of its energy infrastructure is a 10-megawatt solar power plant. That solar power plant is complemented by extensive rooftop photovoltaic installations across the city. These solar arrays harness the abundant sunlight in Abu Dhabi to generate clean electricity.
This commitment to renewable energy not only reduces greenhouse gas emissions but also demonstrates the feasibility of large-scale solar power integration in urban environments. By leveraging cutting-edge solar technology, Masdar City sets a benchmark for sustainable energy practices in arid regions.
Water Management
Safe and effective water management is another foundational element of Masdar City’s design. The city employs state-of-the-art recycling systems to treat and reuse water, which reduces the demand for fresh water. Efficient usage is further ensured through the implementation of smart irrigation systems and water-saving fixtures in buildings.
Fuel your creative fire & be a part of a supportive community that values how you love to live.
subscribe to our newsletter
*please check your Spam folder for the latest DesignDash Magazine issue immediately after subscription

Waste Management
Masdar City’s waste management strategy is set to achieve zero waste to landfills by focusing on comprehensive recycling and composting programs. The urban community encourages residents and businesses to segregate waste at its source so they can facilitate efficient recycling processes. Organic waste will be composted to produce nutrient-rich soil, which will then be used in the city’s green spaces and agriculture.
The city will also employ waste-to-energy technologies that convert non-recyclable waste into energy. This should further reduce the city’s landfill dependency.
Transportation
Transportation in this United Arab Emirates city is also designed to minimize environmental impact through the use of innovative technologies and sustainable planning. The city features a limited but operational Personal Rapid Transit (PRT) system consisting of electric, driverless vehicles that provide efficient and eco-friendly mobility. This system reduces the need for private cars while cutting down on emissions and traffic congestion. However, this system is currently limited to a small area within the city and is not as widely used as initially planned. In addition to PRT, the urban layout of Masdar City promotes the use of public transportation and bicycles with well-connected pathways and transit hubs.
Economic and Social Aspects
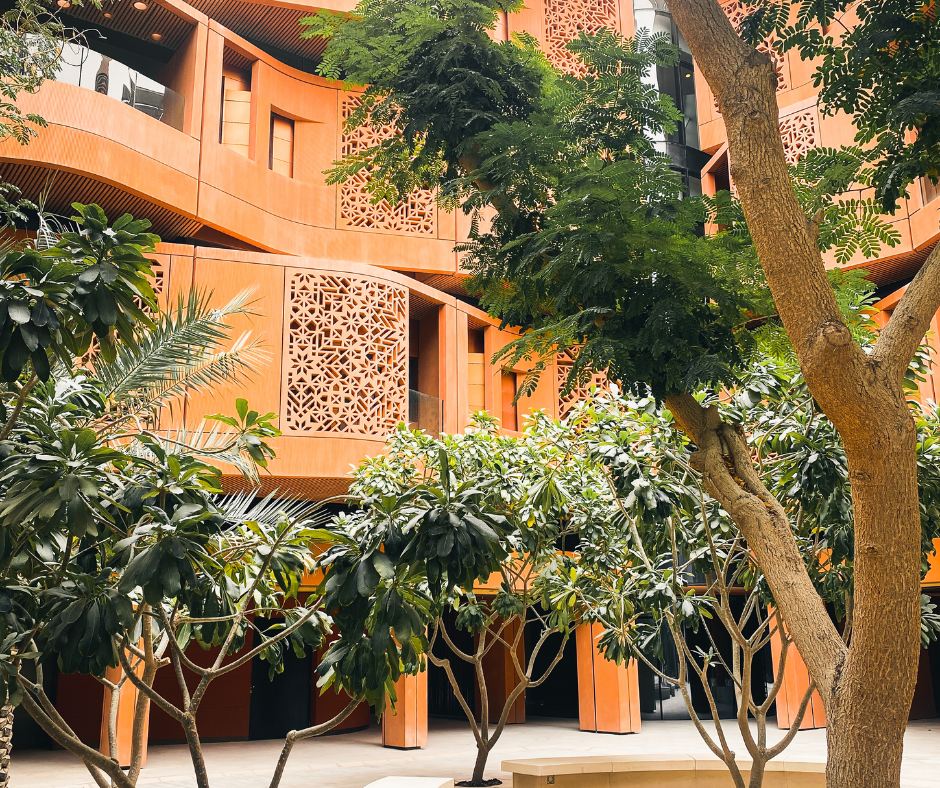

The Masdar City Free Zone provides a variety of economic incentives designed to attract companies in the clean technology and renewable energy sectors. This is the most developed part of the city thus far, and that fact has garnered criticism from those who claim that the city is focused more heavily on business ventures than would-be residents.
Businesses setting up in Masdar City benefit from 100% foreign ownership, tax exemptions, and simplified business registration processes. These incentives make Masdar City an attractive hub for startups and established companies looking to innovate in sustainability.
The free zone status helps foster an ecosystem of innovation that attracts global talent and investment. Masdar City offers state-of-the-art infrastructure and facilities tailored to the needs of technology and research-driven enterprises. With its infrastructure and incentives, Masdar City is slated to become a hot spot for growth and collaboration in the green tech sector.
Community Initiatives
Though this part of the plan is less developed than its economic and research centers, Masdar City’s designers claim that they will build a vibrant community that seamlessly integrates residential, commercial, and recreational spaces while adhering to sustainable living principles. The city is designed to provide a high quality of life for its residents with eco-friendly housing options, green public spaces, and a variety of amenities like schools, healthcare facilities, and retail centers.
As noted above, community planning will prioritize walkability and social interaction through shaded pedestrian pathways, parks, and communal areas that encourage residents to engage with their environment and each other.
Challenges and Criticisms of Masdar City
Cost and Scale

Just two years ago, developers and construction crews broke ground on Masdar City Square, with completion projected for later this year. Unfortunately, the ambitious goals and high costs associated with Masdar City have led to a series of delays and adjustments in the project’s timeline and scale.
Initially envisioned as a fully sustainable city that would serve as a global model for similar initiatives around the world, the project has faced financial challenges that have necessitated scaling back many of its plans. Now, the city won’t be finished until well after 2030. After eighteen years, many have grown weary of the project, with some calling it a “cautionary tale.”
Economic factors like the global financial crisis and fluctuating oil prices have impacted funding and investment. These challenges have slowed construction and led to a phased development approach, with certain features and milestones being postponed or re-evaluated. Despite these setbacks, Masdar City continues to push forward with its core mission of sustainability and innovation, albeit at a modified pace.
Population Density

Masdar City was initially planned to accommodate 50,000 residents and just as many commuters, but actual population growth has been slower than anticipated. Several factors contribute to this slower-than-expected growth, including the high cost of living, limited initial infrastructure, and the ongoing development of essential services and amenities.
As you might imagine, attracting residents to a new, experimental urban environment can be challenging. Efforts are being made to enhance the city’s appeal through the completion of more residential units, expansion of commercial and recreational facilities, and the establishment of a vibrant community life. As these developments progress, Masdar City’s investors hope that the population will grow to meet original expectations.
High Cost of Living and Social Impact
The cost of living in Masdar City is significantly higher than in other parts of Abu Dhabi because of the premium placed on sustainable technologies and high-end housing. As a result, the city has struggled to attract a diverse population and raised concerns about social equity.
Concerns have also been raised about the overall social impact of Masdar City. The displacement of local communities to make way for the city’s development and the limited access for lower-income residents have sparked debate about the project’s inclusivity and social sustainability.
Despite efforts to create a vibrant community, Masdar City’s social scene remains limited compared to other urban centers. The city is still under development, and the lack of diverse entertainment, cultural, and nightlife options has deterred some potential residents.
Environmental Challenges

Its environment also poses major challenges. For example, the accumulation of sand and dust on solar panels can hamper their efficiency. To address this issue, the city currently employs a combination of robotic cleaners and manual cleaning methods to ensure that the panels remain free of dust and operate at optimal efficiency. Regular maintenance is absolutely essential in a desert environment where dust storms and wind-borne sand are common.
Heat and Dust Impact on Buildings
The high temperatures and dust prevalent in Abu Dhabi’s desert environment also pose challenges to building materials and other systems beyond solar panels. To mitigate these effects, buildings in Masdar City are constructed with high thermal mass materials and advanced insulation, which help to reduce heat absorption. Its facades are designed to minimize dust accumulation, too. These design considerations help to protect the buildings from the harsh climate while enhancing their energy efficiency.
Air Quality

Dust storms in the region can negatively impact air quality and pose health risks to residents (though few have set down roots in Masdar City to date). To combat this, buildings in Masdar City are equipped with advanced air filtration systems that ensure indoor air remains clean and safe. These systems are essential for maintaining a healthy living and working environment, particularly during frequent dust storms.
Sand Erosion
Sand erosion is another environmental challenge affecting the stability of structures and landscaping in Masdar City. To counteract this, the city promises to observe sustainable landscaping practices. In addition to selecting native plants that are well-adapted to the desert environment and help stabilize the soil, the city will add green spaces and wind barriers. Building placements are also specifically designed to minimize the impact of sand movement.
True Sustainability
The decision to build a new city in the desert has raised important questions about environmental sustainability in addition to social sustainability criticisms. Critics argue that the resources required for construction, water management, and maintaining a comfortable living environment in such a harsh climate negate some of the environmental benefits. The reliance on energy-intensive technologies, even if powered by renewables, raises questions about the project’s overall carbon footprint.
Final Thoughts on the Future of Masdar City and Similar Initiatives
By integrating cutting-edge renewable energy technologies, innovative architectural designs, and comprehensive sustainability practices, Masdar City was intended to model the feasibility and benefits of sustainable urban living. However, delays and criticisms have taken the wind out of its developers’ sails to a certain degree. In spite of major challenges related to cost, scale, and environmental conditions, the city has pressed forward.
Its investors repeatedly double-down on their commitment to creating a sustainable, low-carbon community. We can only hope that Masdar City will indeed set a much-needed benchmark for eco-conscious development, proving that with dedication and innovation, the vision of a sustainable future can indeed become a reality.
Written by the DesignDash Editorial Team
Our contributors include experienced designers, firm owners, design writers, and other industry professionals. If you’re interested in submitting your work or collaborating, please reach out to our Editor-in-Chief at editor@designdash.com.