What is Functional Medicine, and How Can It Help Women?
Summary
Functional medicine offers a personalized, holistic approach to healthcare, focusing on identifying and addressing the root causes of diseases rather than just treating symptoms. It emphasizes a patient-centered rather than a disease-centered approach, incorporating the latest in genetic science, systems biology, and understanding of environmental and lifestyle factors. For women, functional medicine can be particularly beneficial, addressing hormonal imbalances, reproductive health, menopause, chronic stress, and lifestyle-related health issues. By tailoring treatments to the individual’s unique conditions, history, and health goals, functional medicine aims to optimize women’s health, promote wellness, and prevent diseases through a comprehensive, integrative approach.
Reflection Questions
- How does the concept of functional medicine differ from your current understanding of healthcare, and what aspects of it appeal to you the most?
- In what ways do you think a more personalized, root-cause approach to health could address any ongoing health concerns you have?
- Have you experienced health issues that you feel have not been fully resolved or understood through conventional medicine? How might functional medicine offer a different perspective or solution?
Journal Prompt
Reflect on your relationship with your healthcare providers. Do you feel heard and understood? How might a more collaborative, patient-centered approach, like that of functional medicine, change your healthcare experience?
Women seeking a more holistic and comprehensive approach to their health can greatly benefit from the principles of functional medicine. This patient-centered approach goes beyond merely treating symptoms to explore the root causes of health issues, offering a pathway to not only address common women’s health concerns—such as hormonal imbalances, reproductive health issues, and chronic conditions—but also to enhance overall well-being.
By considering the unique interplay of genetics, lifestyle, and environmental factors in each individual, functional medicine empowers women with personalized strategies that encompass nutrition, stress management, physical activity, and integrative therapies. This tailored approach helps ensure that each woman’s health journey is as unique as her own life story, promoting optimal health, vitality, and resilience throughout all stages of life. Learn more about functional medicine below.
What Exactly is Functional Medicine?

Functional medicine is a systems biology-based approach that aims to identify and address the root causes of disease. Unlike traditional medicine, which often focuses on treating symptoms, functional medicine seeks to understand and treat the underlying causes of a patient’s health issues by considering the body as an interconnected whole. It emphasizes a patient-centered approach rather than a disease-centered one.
A functional medicine practitioner will typically spend more time with their patients, gathering detailed histories and looking at the interactions among genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors that can influence long-term health and complex, chronic disease. In this way, functional medicine supports the unique expression of health and vitality for each individual.
Key aspects of functional medicine include personalized care tailored by a functional medicine doctor the the individual’s needs, a scientific and integrative approach to medicine, a focus on patient empowerment, and commitment to discovering root causes of chronic illness. Functional medicine is used to treat a wide range of health issues, including chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, autoimmune diseases, and mental health disorders.
Though still considered an alternative medicine approach, functional medicine services are increasingly recognized for their potential to improve health outcomes by addressing the complexities of individual health. To learn more, consult resources provided by the Institute for Functional Medicine.
How Do Functional Medicine Practices Differ from Conventional Medicine?

Functional medicine differs from traditional (conventional) medicine in several fundamental ways, primarily in its approach to diagnosing, treating, and understanding diseases and health conditions. Below are some key differences between functional medicine practitioners and traditional western doctors.
Approach to Disease and Health

Functional medicine doctors focus on identifying and addressing the root causes of diseases by examining one’s lifestyle and medical history. This practice views the body as an interconnected system, recognizing that a dysfunction in one part can affect the whole body. The goal is to restore balance and support the body’s natural healing mechanisms.
Traditional medicine focuses on treating symptoms and diseases using standardized methodologies. It often views the body as a collection of independent organs divided into specialties.
Patient-Centered vs. Disease-Centered
Functional medicine emphasizes a patient-centered approach, considering patients’ unique histories, genetics, and lifestyle factors. Treatments are personalized and holistic, aiming to optimize overall health and well-being.
Traditional Medicine often operates on a disease-centered model, focusing on the disease itself rather than the individual patient. Treatment plans are more likely to follow established protocols that are applied broadly to anyone with the same condition.
Use of Diagnostic and Treatment Methods
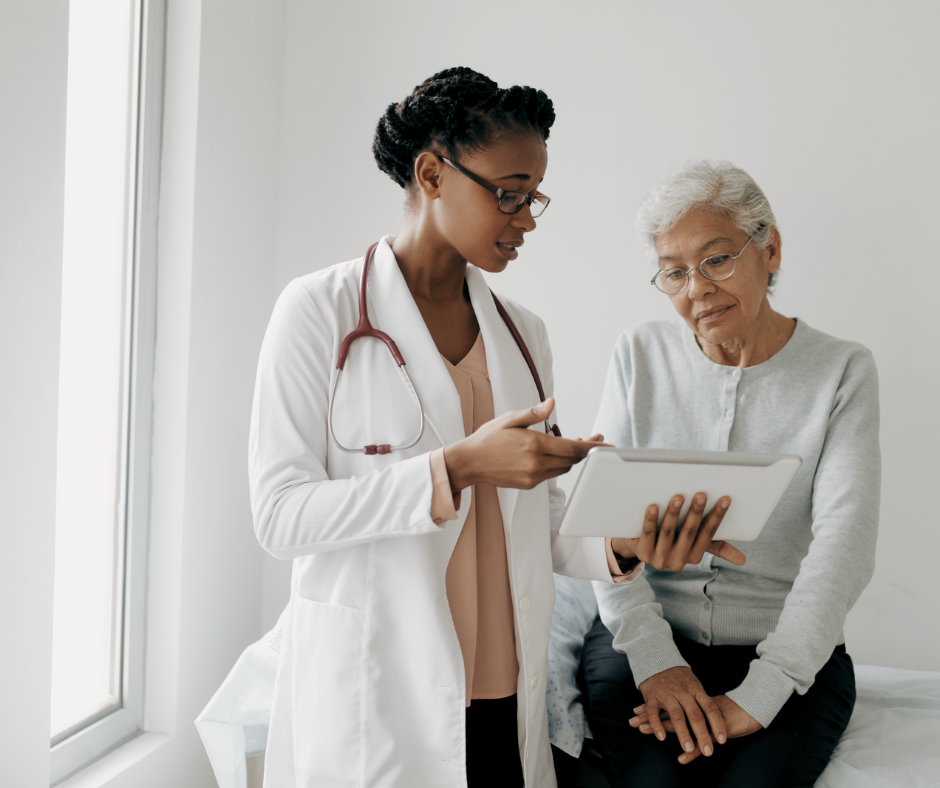

Functional medicine providers use a wide range of diagnostic tools, including detailed health histories, advanced laboratory testing, and genetic information to uncover the complexities of a patient’s condition. Treatments may include lifestyle interventions, nutritional support, detoxification programs, and stress-management techniques alongside conventional treatments.
Traditional medicine relies on standard diagnostic criteria and treatments such as pharmaceuticals and surgery. While effective for acute and emergency care, this approach may not always address the underlying causes of chronic diseases.
Emphasis on Lifestyle and Prevention
Functional medicine places a strong emphasis on diet, exercise, and lifestyle as central components of both treatment and prevention. Will a functional medicine doctor treat your underlying medical issues? Yes, but they also aim to empower patients to take an active role in their health through education and lifestyle modifications.
While there is a growing focus on prevention and lifestyle factors, traditional medicine has historically placed more emphasis on treating disease after it occurs rather than on early intervention and lifestyle modification to prevent diseases.
Integration of Alternative Therapies
Functional medicine often integrates alternative or complementary therapies (such as herbal medicines, acupuncture, and mindfulness practices) into treatment plans. These are chosen based on evidence of their effectiveness and safety, and how well they address the individual’s unique needs.
Traditional medicine is more cautious about integrating alternative therapies, typically relying on treatments that are widely accepted in the scientific community and have undergone rigorous clinical trials.
Collaborative Care

Functional medicine encourages a collaborative care model, often involving a team of health care providers including doctors, nutritionists, health coaches, and therapists to address all aspects of a patient’s health by jointly examining the patient’s comprehensive medical history.
Traditional care is also collaborative but tends to be more compartmentalized, with specialists focusing on their area of expertise, sometimes leading to fragmented care.
Working with a Functional Medicine Doctor or Health Coach
When considering working with a functional medicine doctor and/or a functional medicine health coach, there are several important aspects women should be aware of to ensure they receive comprehensive and effective care. Here’s what to keep in mind.
Understanding the Roles

A functional medicine doctor is a licensed physician who has additional training in functional medicine. They can diagnose conditions, order and interpret tests, and prescribe medications or treatments based on a holistic view of your health.
A Functional Medicine Health Coach typically works alongside functional medicine doctors to support patients in implementing lifestyle changes and following through on treatment plans. While they do not diagnose conditions or prescribe treatments, they play a crucial role in motivating, educating, and guiding patients on their journey to better health.
Integration with Conventional Care
Functional medicine is not intended to replace traditional primary care but to complement it. A functional medicine doctor or health coach can work in tandem with your primary care physician and other specialists to provide a more integrated approach to your health.
It’s essential to maintain a relationship with a PCP for routine health screenings, vaccinations, acute care, and referrals to specialists. Your PCP can also help coordinate care between different healthcare providers.
Choosing the Right Provider

Look for providers with reputable credentials in functional medicine (such as certification from the Institute for Functional Medicine) and experience in treating your specific health concerns. Ensure that the provider’s philosophy and approach align with your health goals and preferences. Consider whether the functional medicine doctor or health coach has a network of other healthcare professionals they collaborate with, including specialists and primary care providers.
Understanding the Functional Medicine Matrix

The Functional Medicine Matrix is a central tool used within the field of functional medicine to assist practitioners in organizing and prioritizing a patient’s health issues. This comprehensive framework is designed to facilitate a thorough understanding of a patient’s health status by viewing their conditions and symptoms through the lens of the body’s core biological systems and the various factors that influence these systems. The matrix helps in identifying the root causes of health issues and developing personalized treatment plans.
Components of the Functional Medicine Matrix
The Seven Core Clinical Imbalances
- Assimilation: Includes digestion, absorption, microbiota/GI flora, and respiration.
- Defense and Repair: Focuses on inflammation, infection, and immune function.
- Energy: Pertains to energy regulation and mitochondrial function.
- Biotransformation and Elimination: Concerns detoxification and waste elimination.
- Transport: Involves the cardiovascular and lymphatic systems.
- Communication: Encompasses endocrine, neurotransmitter, and immune messengers.
- Structural Integrity: Relates to the physical framework of the body, including the skeletal system and membranes.
The Antecedents, Triggers, and Mediators (ATMs)
- Antecedents: Genetic, physical, and psychosocial factors that predispose an individual to illness.
- Triggers: Events or exposures that provoke the manifestations of illness.
- Mediators: Factors that contribute to the continuation or exacerbation of illness.
The Lifestyle Factors

These include nutrition, exercise, sleep/rest, stress, relationships, and networks. They are crucial for maintaining health and are often the focus of personalized interventions in functional medicine.
Purpose and Use
The matrix serves as a comprehensive framework for understanding the multifactorial nature of chronic diseases, emphasizing the interconnections between different body systems and the lifestyle factors that influence them. By identifying and addressing the underlying causes of disease specific to each patient, the matrix helps practitioners develop personalized treatment plans that go beyond symptomatic relief. It provides a common language and framework for practitioners to communicate about patient care, ensuring a cohesive and integrated approach.
Implementation
In practice, the Functional Medicine Matrix encourages practitioners to take detailed patient histories and perform comprehensive evaluations. This process not only considers physical symptoms but also explores environmental exposures, genetic predispositions, lifestyle factors, and psychosocial contributors to health. The matrix helps in organizing this information, guiding the diagnostic process, and prioritizing treatment strategies that address the root causes of illness.
The Functional Medicine Model and Women’s Chronic Health Conditions

Alongside other members of your care team, a functional medicine provider can offer a comprehensive approach to managing and treating women’s health issues like Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD), endometriosis, Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), and other health concerns. This approach is particularly beneficial for these conditions, which are often complex and multifactorial, involving hormonal imbalances, immune system dysfunctions, genetic factors, and environmental influences. Here’s how functional medicine can help.
Personalized Treatment Plans
Understanding Individual Differences: Recognizes that each woman’s genetic makeup, lifestyle, and environmental exposures are unique, and these factors can influence the severity and manifestation of symptoms.
Tailored Therapies: Develops personalized treatment plans that may include dietary changes, lifestyle modifications, supplements, and other integrative therapies based on individual needs.
Addressing Root Causes

Hormonal Imbalances: Functional medicine seeks to identify and correct hormonal imbalances that often underlie conditions like PMDD, PCOS, and endometriosis. This may involve comprehensive hormone testing and natural or bioidentical hormone therapies.
Inflammation and Immune Function: Many reproductive health issues involve inflammatory processes or autoimmune responses. Functional medicine approaches include dietary interventions, supplements, and lifestyle changes aimed at reducing inflammation and supporting immune health.
Gut Health: The gut microbiome plays a significant role in overall health, including hormonal balance and immune function. Functional medicine often includes strategies to improve gut health, such as probiotics, dietary changes, and addressing gut dysbiosis.
Integrated Care Approach
Combining Conventional and Alternative Therapies: Functional medicine integrates conventional medical treatments with complementary therapies, such as acupuncture, herbal medicine, and nutritional therapy, offering a holistic approach to treatment.
Collaborative Care: Often involves collaboration with a team of healthcare providers, including specialists in women’s health, nutritionists, and integrative medicine practitioners, to provide comprehensive care.
Focus on Lifestyle and Prevention

Diet and Nutrition: Provides guidance on nutrition to support hormonal balance, reduce inflammation, and manage symptoms. This may include diets rich in phytoestrogens, omega-3 fatty acids, and anti-inflammatory foods.
Stress Management: Stress is a significant factor in many women’s health issues. Functional medicine incorporates stress reduction techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, and counseling.
Physical Activity: Recommends appropriate exercise regimes that can help manage weight, improve insulin sensitivity, and support overall hormonal balance.
Empowering Patients

Coaches and doctors at a functional medicine center will educate patients about their conditions and the factors that affect their health, empowering them to take an active role in their treatment and make informed decisions about their care. This is particularly important for women who are often gaslighted about their medical issues.
Final Thoughts: Key Considerations for Women Considering a Functional Medicine Approach
Be prepared for a comprehensive assessment of your health, including detailed questionnaires about your lifestyle, diet, exercise, sleep patterns, and mental health. This holistic view helps the doctors that practice functional medicine identify underlying causes of health issues. Functional medicine often requires a significant time commitment, both in terms of initial consultations, follow-up visits, and implementing lifestyle changes. Be prepared to actively participate in your health improvement process.
Functional medicine visits may not always be covered by insurance plans, leading to out-of-pocket expenses for consultations, tests, and treatments not typically included in conventional healthcare. Always inquire about costs upfront and check with your insurance provider regarding coverage. While functional medicine is grounded in science, some approaches or treatments might be considered experimental or not widely accepted in conventional medicine. Ask your functional medicine doctor about the evidence supporting any recommended treatments or interventions.
A key goal of functional medicine is to empower you to take an active role in your health. This involves education about your condition and the factors affecting it, as well as guidance on making sustainable lifestyle changes. Effective communication between you, your functional medicine team, and your primary care physician is crucial for coordinating care and ensuring all aspects of your health are addressed.