From Africa to the Americas: The State of AI Legislation Around the World
Summary
This article explores the varied approaches countries take towards AI regulation, reflecting on the ethical, safety, and security concerns of AI use across different industries and public sectors. It provides an overview of legislative efforts in regions like the EU, UN, Japan, China, Canada, the US, the Middle East, South America, and African nations, highlighting the global efforts to balance AI’s potential benefits with its risks.
Reflection Questions
- Considering the diversity in AI legislation globally, what might be the challenges and benefits of international cooperation on AI standards?
- How do cultural and societal values influence a country’s approach to AI regulation?
- Reflect on the balance between innovation and ethical considerations in AI development. How should policymakers address this?
Journal Prompt
Think about the impact of AI on your daily life and the broader society. Write about how you believe AI should be regulated in your own country, considering both the protection of individual rights and the encouragement of technological advancement.
As nations grapple with the rapid evolution of artificial intelligence (AI), the legislative landscape from America to Japan reflects a mosaic of strategies and concerns. In this article, we assess the varied state of AI legislation around the world, exploring how different countries are navigating the challenges and opportunities presented by AI. From comprehensive frameworks in the European Union to targeted initiatives in the United States and pioneering strategies in Asia, we uncover the global efforts to regulate a technology that promises to reshape every aspect of society. Read on to learn more about AI legislation here and abroad!
Industries Currently Impacted by the Use of Artificial Intelligence
Office and Administrative Support
AI-driven automation is poised to transform the office and administrative support sector significantly. Routine tasks such as data entry, scheduling meetings, and document management are ideal candidates for AI automation due to their repetitive and predictable nature.
AI can streamline these tasks, making administrative processes more efficient and freeing up human employees for more complex and creative tasks. For instance, AI-powered virtual assistants can manage calendars, set reminders, and even handle email correspondence, thereby increasing productivity and reducing the need for manual intervention in these areas.
Healthcare
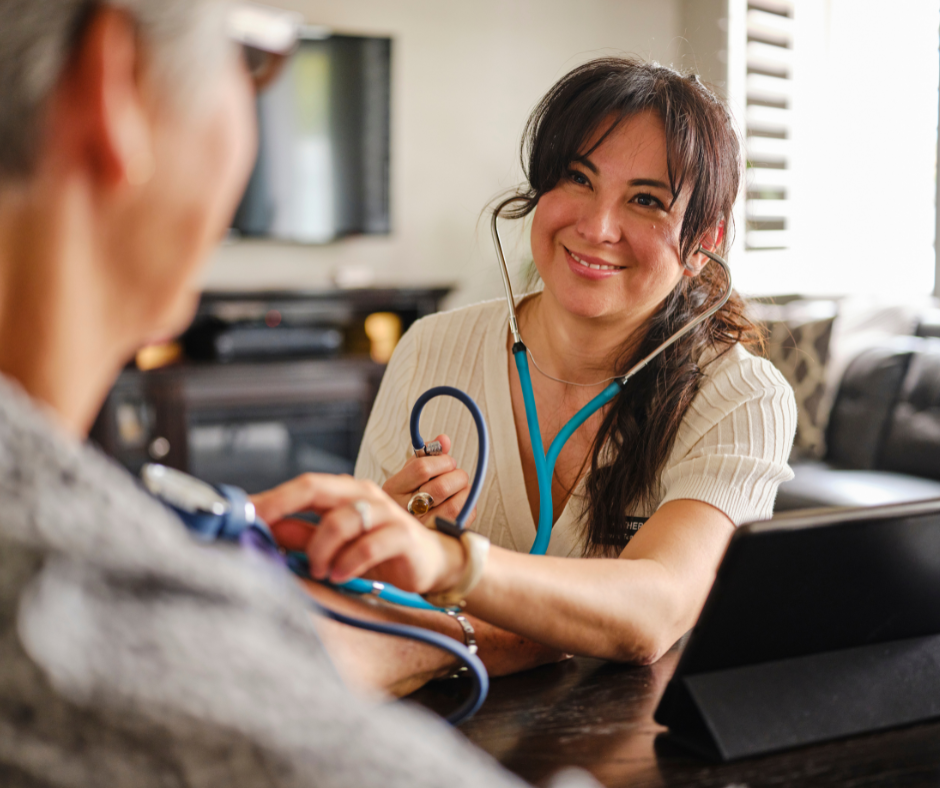


In healthcare, AI is making a substantial impact by enhancing efficiency and precision in various areas, including virtual nursing, administrative workflow assistance, automated systems in data entry, and robot-assisted surgery. AI applications like IBM Watson are advancing disease diagnosis and treatment plans by analyzing vast amounts of medical data to identify patterns and suggest diagnoses and treatments that might not be apparent to human practitioners.
This can lead to more accurate and earlier diagnoses, particularly for complex conditions. Moreover, robot-assisted surgery allows for minimally invasive procedures, reducing recovery times and improving surgical outcomes.
Interior Design
AI tools are revolutionizing the way designers visualize, plan, and execute their ideas. These tools leverage AI to analyze patterns, understand user preferences, and generate creative design solutions. For interior design, specifically, AI applications range from generating room layouts and furniture placement to offering 2D and 3D visualization and personalized design recommendations. Platforms like Homestyler and Midjourney exemplify how AI can provide both professionals and enthusiasts with powerful design capabilities, enhancing creativity and efficiency.
Photography
Photography and film are also undergoing transformations due to AI. Generative AI tools have shown potential in creating written and visual content of high standards, impacting creative jobs by automating some tasks and offering new tools for creation. While this presents opportunities for innovation and efficiency in content creation, it also poses challenges, such as the risk of “hallucinating” or fabricating information by AI tools. The arrival of creative AI tools in these domains suggests a future where automation and human creativity coexist, potentially automating some aspects of creative jobs while also offering new avenues for artistic expression.
Agriculture
AI technology is revolutionizing agriculture by optimizing the use of resources and increasing the quality and quantity of produce. Innovations such as weed control robots, harvesting robots, and drones equipped for crop and soil monitoring are introducing precision agriculture.
These AI-driven tools can analyze data on soil health, moisture levels, and pest presence to optimize planting, watering, and treating crops, thereby increasing yield and reducing the environmental impact of farming practices. The industry has yet to use an automated decision system, but rather uses AI to inform.
Music and Performance


AI is increasingly being used to create music, offering tools for composition, lyric writing, and even performing music in various artists’ styles. This technological evolution has sparked debates about creativity and the role of AI in music production. While AI can generate music that competes with human-created content in quality, concerns about originality and artistic integrity persist. The technology is at a point where it can produce compositions in the style of specific artists, raising questions about the authenticity and the potential for replacing human creativity.
Manufacturing
In the manufacturing industry, AI is improving efficiency across the board by enhancing design time, reducing waste, and facilitating predictive maintenance. By analyzing data from the manufacturing process, AI can identify inefficiencies and predict when machines are likely to fail, allowing for preventative maintenance that minimizes downtime. AI can also optimize production lines for efficiency, ensuring that resources are used effectively and that products are produced at the highest quality.
Fashion


AI is transforming the fashion industry by improving inventory management, personalizing customer experiences, and enhancing online shopping. AI algorithms can analyze trends and consumer behavior to predict demand, ensuring that retailers stock the right products in the right quantities. Virtual stylists and smart assistants can offer personalized shopping experiences by recommending products based on the customer’s style preferences and past purchases, improving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Legal, Architecture, Engineering, and Sciences
These sectors are experiencing a high degree of automation potential with AI expected to automate tasks such as legal analysis and engineering tasks. AI can analyze legal documents and case law at a speed that is impossible for human lawyers, identifying relevant precedents and suggesting arguments. In architecture and engineering, AI can optimize designs for efficiency and sustainability, analyzing countless design variations to find the optimal solution.
Public Sector, Retail, Financial Services, and More
AI’s versatility means it’s being used across a wide range of sectors for diverse tasks. In the public sector, AI is improving the efficiency of services, from predicting arrival times of public transport to optimizing resource allocation. In retail and financial services, AI is used for analyzing consumer behavior, personalizing services, and improving decision-making. For instance, AI can help in fraud detection by analyzing transaction patterns to identify anomalies that may indicate fraudulent activity.
AI Systems Around the World: Global Ethics, Safety, and Security Concerns
Why do we need AI regulation? AI introduces several ethical, safety, and security concerns across different domains, including privacy, bias, accountability, transparency, and economic impacts. Given AI’s transformative potential and associated risks, there’s a pressing need for responsible technology use that considers ethical, safety, and security implications.
This involves aligning AI development and deployment with human values, ensuring transparency, mitigating biases, and establishing clear accountability frameworks. It might also involve implementing regulatory and compliance frameworks unique to AI. Engaging in ongoing discussions, setting ethical guidelines, and adopting best practices are crucial steps towards responsible AI use that benefits society as a whole.
Biases in Collection and Interpretation of Data
One of the primary challenges is the statistical nature of AI, which can perpetuate existing biases found in historical data. This can lead to unfair or discriminatory outcomes, especially in areas like cybersecurity, where biased AI might unfairly target certain groups. There is concern that AI could discriminate against people based on national origin, sexual orientation, religious affiliation, and more. Such abusive data practices are of grave concern and one important reason why many argue that we must regulate AI.
The accountability for decisions made by AI systems is another significant concern, as it’s often unclear who should be responsible when an AI system makes an error. Transparency is also a critical issue, with many AI models acting as “black boxes,” making it difficult to understand or explain their decisions. This lack of transparency can erode trust and complicate accountability.
Cybersecurity Issues
In the context of cybersecurity, AI-driven systems can inadvertently capture sensitive information, raising privacy concerns. Moreover, the automated nature of AI in cybersecurity can lead to job displacement, adding economic impacts to the list of ethical dilemmas. Balancing security with privacy and ensuring fair, unbiased decision-making are critical challenges that need addressing as AI systems become more integrated into cybersecurity efforts.
Fuel your creative fire & be a part of a supportive community that values how you love to live.
subscribe to our newsletter
Deepfakes and Misrepresentation
The risk of deepfaking and the potential for generative artificial intelligence (AI) systems to create fake information, including news and media, has prompted significant concern across various sectors globally. The advanced technology behind deepfakes allows for the creation of highly realistic, fabricated images, audio, and videos using AI algorithms. As these deepfakes become increasingly indistinguishable from authentic content, they pose a substantial threat to privacy, security, and the integrity of information.
High-profile cases have highlighted the severe implications of deepfake technology, particularly involving public figures. For instance, the unauthorized creation and distribution of sexually explicit AI-generated images of celebrities have caused significant harm and drawn attention to the challenges in controlling such content. Deepfake technology’s ability to forge hyper-realistic content presents novel challenges to existing legal frameworks, often outpacing the capacity of current laws to effectively manage these advanced technological manipulations.
Parsing the Ethical Use of AI
The ethical use of AI extends beyond technical and security aspects, impacting societal norms and human judgment. Concerns about AI systems replicating human biases and potentially automating discrimination are significant. The technology’s ability to analyze vast amounts of data can offer benefits, such as improved access to capital for small businesses, by reducing information opacity.
However, there’s a risk that AI-driven decisions might inadvertently perpetuate historical biases and injustices, such as redlining. The challenge lies in ensuring that AI systems are designed and deployed in a way that enhances fairness and equity without sacrificing efficiency or innovation.
How Do We Regulate AI? Examining Recent AI Legislation Across the Globe
Governments around the world have been actively considering and implementing AI legislation to address the challenges and opportunities presented by this rapidly evolving technology. Let’s take a look at key developments in AI regulation across different regions.
European Union


The EU has taken significant steps with the AI Act, aiming to regulate the development and application of AI technologies. This legislation focuses on high-risk AI systems, demanding transparency, accountability, and measures to mitigate biases. It categorizes AI applications based on their risk levels, imposing stricter requirements on those deemed high-risk, including systems like OpenAI’s GPT-4 and Google’s Gemini. The Act also introduces measures to ban certain uses of AI, such as facial recognition databases and emotion recognition technology in specific contexts. Furthermore, the EU is working on the AI Liability Directive to allow financial compensation for harms caused by AI technology. This comprehensive approach sets a precedent for global AI regulation, influencing standards beyond its borders.
The UN
On the international stage, the United Nations (UN) is emphasizing the need for global governance of AI to ensure that the technology benefits all of humanity while mitigating risks. The UN’s AI Advisory Body, led by Carme Artigas, has advocated for global regulations to address the challenges posed by AI, including issues of trust and the potential for confusion between human and machine-generated content. The UN aims to foster a global consensus on AI governance that promotes innovation, protects fundamental human rights, and avoids exacerbating a global AI divide.
Japan


Japan is preparing to introduce legislation to regulate generative AI technologies in 2024, focusing on issues like disinformation and rights infringements. Preliminary rules may include penal regulations for developers of foundational AI models, aligning with efforts in the EU and other regions to address the challenges posed by AI.
China
China’s approach to AI regulation has been more fragmented, with specific rules for different types of AI applications, such as algorithmic recommendation services and deepfakes. However, China announced plans to draft a unified AI law covering all aspects of artificial intelligence, signaling a move towards more comprehensive regulation. This proposed law aims to establish a national AI office and requires AI companies to conduct yearly “social responsibility reports” and adhere to a “negative list” of high-risk AI research areas requiring government approval.
Canada
Canada is addressing AI regulation through the Artificial Intelligence and Data Act (AIDA), introduced as part of Bill C-27. AIDA aims to ensure AI systems used by Canadians are safe, protect external consumer data from threats, and respect Canadian values, introducing a framework for responsible AI adoption. It emphasizes a risk-based approach, focusing on high-impact AI systems and includes provisions for human oversight, transparency, and accountability. The Act also criminalizes reckless AI use causing serious harm.
The Canada Elections Act also contains language that may apply to deepfakes, and Canada has made efforts to curb the negative impacts of deepfakes, including its plan to safeguard Canada’s 2019 election and the Critical Election Incident Public Protocol, a panel investigation process for deepfake incidents.
The United States


In the United States, AI regulation is evolving at both the federal and state levels, reflecting a growing recognition of the technology’s impact across various sectors. The US has taken a fragmented approach to AI regulation, with individual states enacting their own laws focusing on AI transparency, accountability, and impact assessments.
The National AI Initiative Act of 2021 created a framework to coordinate AI activities across federal agencies. Efforts are ongoing at the national level to introduce comprehensive AI legislation, including the Algorithmic Accountability Act of 2022, which would mandate impact assessments for automated decision-making processes. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has been proactive in addressing AI-related discrimination and unfair practices, even without specific AI regulations.
State-level initiatives are particularly diverse, highlighting the local nuances of AI application and the specific concerns of state residents. Let’s take a closer look at how US states plan to address AI in mental health services, financial and lending services, government, media, and more.
State-Specific Regulations and Initiatives
California is at the forefront of AI regulation, with several pieces of legislation focused on discrimination, safety, transparency, and the regulation of automated decision-making technology (ADMT). California’s efforts are comprehensive, targeting AI’s application in the public and private sectors, including employment and consumer protection.
Colorado and Connecticut have implemented consumer privacy acts that include provisions related to AI, such as the right to opt-out of profiling and requirements for data risk assessments. Both states have also proposed bills to regulate the use of “deepfakes” in political advertising, reflecting a concern over the potential misuse of AI in elections. Their legislation should protect consumers from unsafe or ineffective systems associated with artificial intelligence technology.
Nevada has considered creating an Emerging Technologies Task Force, which would report on the impact of generative artificial intelligence models across the state. This bill would not technically regulate artificial intelligence, but would keep citizens more informed and somewhat protect consumers by making them more aware. Florida and Georgia are considering legislation that would require political campaigns to disclose the use of AI in advertisements, aiming to address concerns over deceptive practices in political advertising.
Broader Trends and Federal Level Initiatives
At the federal level, agencies like the FTC have issued warnings and guidance on AI-related products and services, emphasizing the importance of avoiding false claims and understanding the inherent risks and limitations of AI technologies. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has also released an AI Risk Management Framework, providing a voluntary guide for organizations to manage risks related to each generative artificial intelligence system and promote trustworthy artificial intelligence systems.
State legislative efforts are addressing a wide range of topics, including predictive policing technologies, facial-recognition technologies by police departments, consumer-focused rights, employment-related issues, and healthcare-related issues. For instance, Illinois and New York City have enacted legislation addressing the use of AI in video interviews and automated employment decision tools.
Advisory Bodies and Ethical Considerations
Several states have established advisory bodies, such as task forces and commissions, to study AI and recommend policies. These efforts aim to address employment, healthcare, education, and election issues related to AI. For example, Vermont’s Artificial Intelligence Task Force led to the establishment of the state’s Division of Artificial Intelligence.
Moreover, states are increasingly focusing on data privacy and the potential for AI to exacerbate societal discrimination, with legislation proposed or passed in states like Colorado and Massachusetts aimed at preventing algorithmic discrimination in insurance and employment.
As AI continues to evolve, the regulatory landscape at both the state and federal levels is likely to grow more complex, reflecting ongoing efforts to balance innovation with ethical considerations and consumer protection.
The Middle East


Saudi Arabia is pioneering AI regulation in the Gulf Region with its proposed new Intellectual Property Law, which is one of the first in the Middle East to include IP created by Artificial Intelligence. This law reflects Saudi Arabia’s vision to maximize data and AI’s contribution to realizing the objectives of Vision 2030.
UAE and GCC Countries: The UAE and other Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries are focusing on adopting AI in various sectors, including energy, materials, and retail. However, there is a recognized need for building the necessary AI muscle across strategy, organization and talent, data and technology, and adoption and scaling. The UAE has yet to introduce mandatory regulations governing AI use but has developed BRAIN, a framework to ensure that the country’s AI initiatives remain ethical and responsible.
South America
Regulations in South America are evolving, with countries like Brazil developing their AI strategy focusing on ethical and transparent use of AI, protecting personal data, and promoting the digital economy. However, specific legislation and regulatory details are still emerging and may vary significantly between countries. There isn’t a unified approach across South America yet, and countries are at different stages of considering and implementing AI regulations.
African Nations
African nations are actively participating in the global AI regulation conversation. Countries like Mauritius, Egypt, Kenya, Tunisia, Botswana, and Rwanda have developed strategies or encouraged AI research and adoption. However, the continent faces challenges due to varying levels of technology advancement. Experts suggest Africa’s approach to AI regulation should be pragmatic, focusing on policies to guide AI development before considering comprehensive legislation like the EU’s AI Act.
Final Thoughts on the Regulation and Use of Artificial Intelligence
Across the globe, from America to Japan, AI regulations are as diverse as the technologies it aims to govern. Our world is clearly in cautious negotiation with its future, crafting laws to harness AI’s potential while safeguarding against its risks. As countries chart their courses, the collective endeavor underscores a shared recognition: the imperative to balance innovation with ethical considerations, data privacy, and human rights.
Please leave your opinions on the state of AI legislation in the comments below!
Design Dash
Join us in designing a life you love.
-
All About Our 7-Day Focus & Flex Challenge
Sign up before August 14th to join us for the Focus & Flex Challenge!
-
Unique Baby Names Inspired by Incredible Women from History
Inspired by historic queens, warriors, artists, and scientists, one of these unusual baby names might be right for your daughter!
-
Finding a New 9 to 5: How to Put Freelance Work on a Resume
From listing relevant skills to explaining your employment gap, here’s how to put freelance jobs on your resume.
-
What is Generation-Skipping, and How Might it Affect Sandwich Generation Parents?
The emotional pain and financial strain of generation skipping can be devastating for Sandwich Generation parents.
-
Four Material Libraries Dedicated to Sustainability, Preservation, and Education
From sustainable building materials (MaterialDriven) to rare pigments (Harvard), each materials library serves a specific purpose.
-
Do You Actually Need a Beauty Fridge for Your Skincare Products? (Yes and No.)
Let’s take a look at what dermatologists and formulators have to say about whether your makeup and skincare belong in a beauty fridge.